D185
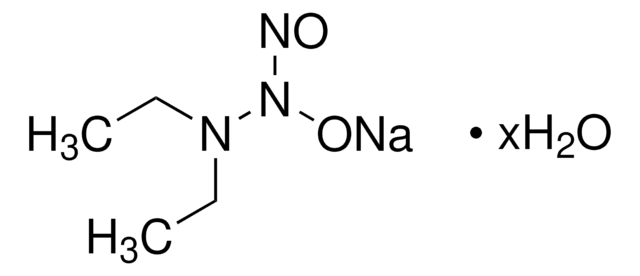
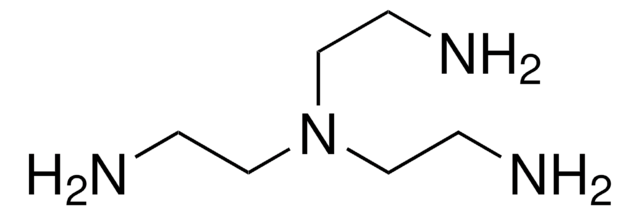
Diethylenetriamine/nitric oxide adduct
≥97% (NMR), solid
Synonym(s):
2,2′-(Hydroxynitrosohydrazono)bis-ethanimine, DETA/NO
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C4H13N5O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
163.18
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Assay
≥97% (NMR)
form
solid
storage condition
desiccated
under inert gas
color
off-white
solubility
H2O: >20 mg/mL
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
NCCN(CC[NH3+])N([O-])N=O
InChI
1S/C4H12N5O2/c5-1-3-8(4-2-6)9(11)7-10/h1-6H2/q-1/p+1
InChI key
PAOXTYJXTPPVHU-UHFFFAOYSA-O
Application
Diethylenetriamine/nitric oxide adduct has been used as nitric oxide (NO) donor:
- to evaluate the direct effects of NO on cell proliferation in ovine trophectoderm (oTr1) cells
- to test its effects on recreating the growth inhibitory effect of NO without the presence of macrophages
- to correlate the outflow function and outflow tract vessel diameter changes with other controls in porcine models
Biochem/physiol Actions
Diethylenetriamine/nitric oxide adduct (DETA/NO) is a NONOate, which has the longest NO?generating half?life in vitro. Inhaled DETA/NO acts as a pulmonary vasodilator in animals and humans. This NO donor releases nitric oxide in solution in a controlled manner. DETA/NO is associated with protein downregulation, upregulation of p53 expression. It enhances p53 post-translational modifications and also downregulates Nanog and Oct4 mRNA.
Caution
Air sensitive
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Self-react. C
Storage Class Code
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Chen Fuh Lam et al.
Clinical and experimental pharmacology & physiology, 30(9), 709-711 (2003-08-28)
1. Inhaled diethylenetriamine nitric oxide adduct (DETA/NO) has been shown to be a selective pulmonary vasodilator in animal and human studies. The aims of the present study were to investigate the effect of DETA/NO on mouse precontracted isolated tracheal smooth
Susannah Waxman et al.
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 59(12), 4886-4895 (2018-10-23)
To correlate outflow function and outflow tract vessel diameter changes induced by nitric oxide (NO). In a porcine anterior segment perfusion model, the effects of a nitric oxide donor (100 μM DETA-NO) on outflow facility were compared with controls (n
Xiaoqiu Wang et al.
Biology of reproduction, 92(3), 75-75 (2015-02-06)
In mammal species, arginine is a multifunctional amino acid required for survival, growth, and development of conceptuses (embryo/fetus and associated extraembryonic membranes) during the peri-implantation period of pregnancy. However, functional roles of arginine with respect to it being a substrate
Elaine K Gregory et al.
American journal of surgery, 202(5), 536-540 (2011-09-29)
S-nitrosothiols (SNO) release nitric oxide (NO) through interaction with ascorbic acid (AA). However, little is known about their combined effect in the vasculature. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of AA on SNO-mediated NO release, proliferation
L De Toni et al.
Journal of endocrinological investigation, 34(10), 738-741 (2012-01-12)
An excess of adipose tissue (AT) in obese individuals is linked to increased cardiovascular risk and mitochondria have been shown to be defective in the muscle and AT of patients with metabolic disorders such as obesity and Type 2 diabetes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service