C4042
Captopril
≥98% (HPLC), powder, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
Synonym(s):
N-[(S)-3-Mercapto-2-methylpropionyl]-L-proline
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Captopril, ≥98% (HPLC), powder
biological source
synthetic
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white to off-white
mp
104-108 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: 100 mg/mL, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless to faintly yellow
originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
C[C@H](CS)C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C9H15NO3S/c1-6(5-14)8(11)10-4-2-3-7(10)9(12)13/h6-7,14H,2-5H2,1H3,(H,12,13)/t6-,7+/m1/s1
InChI key
FAKRSMQSSFJEIM-RQJHMYQMSA-N
Gene Information
human ... ACE(1636) , AGTR1(185) , AGTR2(186) , ECE1(1889)
rat ... Ace(24310)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- to examine the influence of timing of captopril treatment on efficacy in transverse aortic constriction (TAC) mice
- as an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and orally administered to unrestrained Wistar Kyoto rats in an approach to study its effects of angiogenesis inhibition and interdependency with other drugs
- used as a positive control in spectrophotometric assay to study the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Related Content
Discover Bioactive Small Molecules for ADME/Tox
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service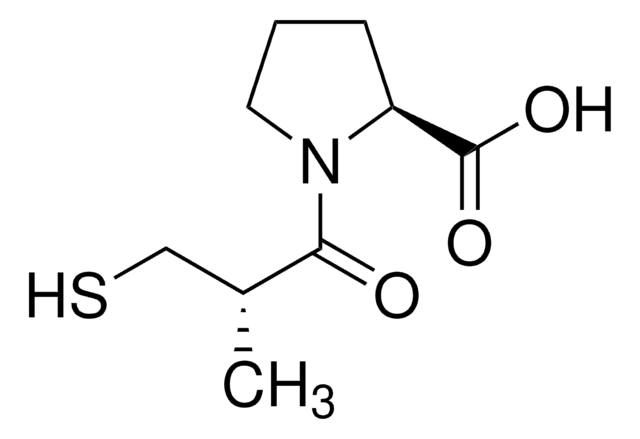

![N-[3-(2-Furyl)acryloyl]-Phe-Gly-Gly](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/225/349/530bc714-b1a8-4fdb-8082-a39329ee730a/640/530bc714-b1a8-4fdb-8082-a39329ee730a.png)