203389
Blebbistatin, Racemic
InSolution, ≥97%, 50 mM in 90% DMSO, reversible inhibitor of nonmuscle myosin II
Synonym(s):
InSolutionBlebbistatin, Racemic
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
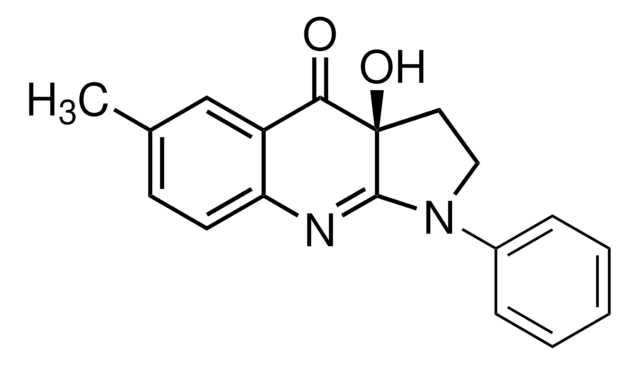
C18H16N2O2
Molecular Weight:
292.33
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥97% (HPLC)
form
liquid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
desiccated (hygroscopic)
protect from light
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
A cell-permeable compound that acts as a selective, potent, and reversible inhibitor of non-muscle myosin II. Inhibits the ATPase and gliding motility of human platelets (≤100 µM) without affecting myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activity. Has been shown to block cell blebbing and to rapidly disrupt directed cell migration and cytokinesis in vertebrate cells. Does not disrupt mitosis or affect contractile ring assembly.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable: yes
Primary Target
ATPase
ATPase
Product does not compete with ATP.
Reversible: yes
Target IC50: <100 µM inhibiting the ATPase and gliding motility of human platelets
Packaging
Packaged under inert gas
Warning
Toxicity: Harmful & Carcinogenic / Teratogenic (E)
Physical form
A 50 mM (5 mg/342 µl) solution of (±)-Blebbistatin (Cat. No. 203390) in 90% DMSO.
Reconstitution
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-20°C).
Other Notes
Shu, S., et al. 2005. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA102, 1472.
Kovacs, M., et al. 2004. J. Biol. Chem.279, 35557.
Straight, A.F., et al. 2003. Science299, 1743.
Cheung, A., et al. 2001. Mol. Biol. Cell Suppl.12, 271a.
Kovacs, M., et al. 2004. J. Biol. Chem.279, 35557.
Straight, A.F., et al. 2003. Science299, 1743.
Cheung, A., et al. 2001. Mol. Biol. Cell Suppl.12, 271a.
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Kevin X Lau et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 2420-2420 (2020-05-18)
Archetypal human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) are widely considered to be equivalent in developmental status to mouse epiblast stem cells, which correspond to pluripotent cells at a late post-implantation stage of embryogenesis. Heterogeneity within hPSC cultures complicates this interspecies comparison.
Catarina Domingues et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 8, 678-678 (2020-09-10)
The mechanical properties of the extracellular environment are interrogated by cells and integrated through mechanotransduction. Many cellular processes depend on actomyosin-dependent contractility, which is influenced by the microenvironment's stiffness. Here, we explored the influence of substrate stiffness on the proteome
Jung Hoon Cho et al.
Science advances, 8(38), eabq8486-eabq8486 (2022-09-24)
Primary cilia are specialized cell-surface organelles that mediate sensory perception and, in contrast to motile cilia and flagella, are thought to lack motility function. Here, we show that primary cilia in human and mouse pancreatic islets exhibit movement that is
Vivek K Gupta et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 220(8) (2021-06-17)
Epithelial cells undergo striking morphological changes during division to ensure proper segregation of genetic and cytoplasmic materials. These morphological changes occur despite dividing cells being mechanically restricted by neighboring cells, indicating the need for extracellular force generation. Beyond driving cell
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service