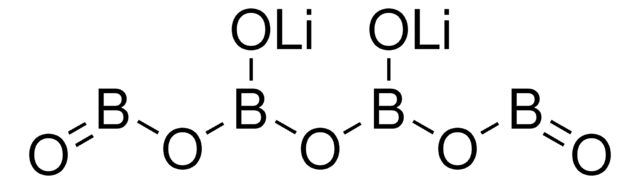
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for X-ray fluorescence analysis
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.0% (acidimetric)
form
solid
pH
9.1 (20 °C, 100 g/L in H2O, slurry)
mp
930 °C
solubility
141.2 g/L
density
2.35 g/cm3 at 20 °C
bulk density
330 kg/m3
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 ppm
phosphate (PO43-): ≤20 ppm
silicate (as SiO2): ≤100 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 ppm
cation traces
Ag: ≤5 ppm
Al: ≤10
Ba: ≤5 ppm
Ca: ≤20 ppm
Cd: ≤5 ppm
Co: ≤5 ppm
Cr: ≤5 ppm
Cu: ≤5 ppm
Fe: ≤10 ppm
Ga: ≤5 ppm
K: ≤10 ppm
Mg: ≤5 ppm
Mn: ≤5 ppm
Na: ≤20 ppm
Ni: ≤5 ppm
Pb: ≤5 ppm
Sr: ≤5 ppm
Zn: ≤5 ppm
storage temp.
2-30°C
InChI
1S/4B.2Li.7H2O/h;;;;;;7*1H2
InChI key
DPYKRXYVXDYLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Linkage
Analysis Note
Chloride (Cl): ≤ 50 ppm
Phosphate (PO₄): ≤ 20 ppm
Silicate (SiO₂): ≤ 100 ppm
Sulfate (SO₄): ≤ 50 ppm
Ag (Silver): ≤ 5 ppm
Al (Aluminium): ≤ 10 ppm
Ba (Barium): ≤ 5 ppm
Ca (Calcium): ≤ 20 ppm
Cd (Cadmium): ≤ 5 ppm
Co (Cobalt): ≤ 5 ppm
Cr (Chromium): ≤ 5 ppm
Cu (Copper): ≤ 5 ppm
Fe (Iron): ≤ 10 ppm
Ga (Gallium): ≤ 5 ppm
K (Potassium): ≤ 10 ppm
Mg (Magnesium): ≤ 5 ppm
Mn (Manganese): ≤ 5 ppm
Na (Sodium): ≤ 20 ppm
Ni (Nickel): ≤ 5 ppm
Pb (Lead): ≤ 5 ppm
Sr (Strontium): ≤ 5 ppm
Zn (Zinc): ≤ 5 ppm
Loss on ignition (1000 °C): ≤ 1.0 %
Bulk density: about 50
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 2
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Related Content
Atomic spectroscopy techniques like AAS, AES, ICP-OES, and ICP-MS identify and quantify elemental composition in samples.
Atomic spectroscopy uses the energy absorbed or emitted by electrons to identify and quantify the elemental composition of a sample. It includes various analytical techniques, such as AAS, AES, FAA, GFAA, ICP-OES, ICP-MS and XRF.
Atomic spectroscopy uses the energy absorbed or emitted by electrons to identify and quantify the elemental composition of a sample. It includes various analytical techniques, such as AAS, AES, FAA, GFAA, ICP-OES, ICP-MS and XRF.
Atomic spectroscopy uses the energy absorbed or emitted by electrons to identify and quantify the elemental composition of a sample. It includes various analytical techniques, such as AAS, AES, FAA, GFAA, ICP-OES, ICP-MS and XRF.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service