D223204
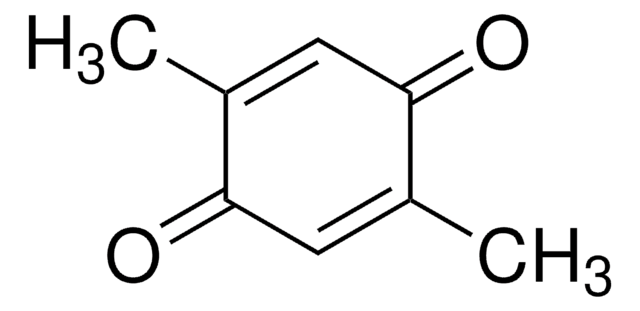
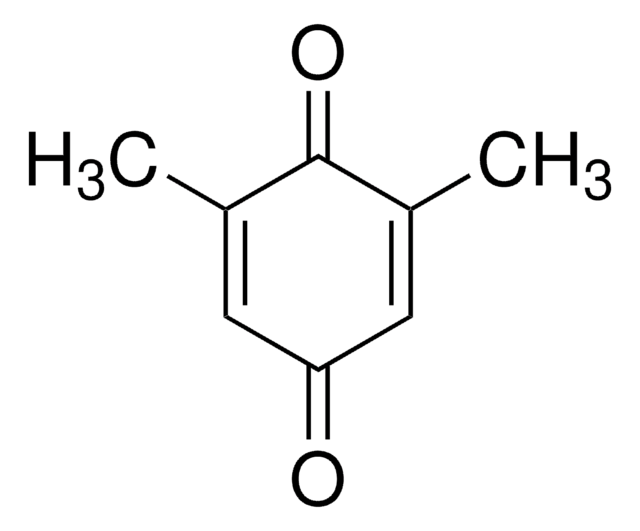
Duroquinone
97%
Synonym(s):
2,3,5,6-Tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone, Tetramethyl-p-benzoquinone
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C10H12O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
164.20
Beilstein:
1909128
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
97%
form
powder
mp
110-112 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC1=C(C)C(=O)C(C)=C(C)C1=O
InChI
1S/C10H12O2/c1-5-6(2)10(12)8(4)7(3)9(5)11/h1-4H3
InChI key
WAMKWBHYPYBEJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Duroquinone is an organic oxidant that belongs to the class of 1,4-benzoquinones, is used in redox flow Li–O2 batteries.
Application
- Role of Duroquinone in Photosynthetic Research: A study on purple bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers highlighted Duroquinone′s role when incorporated into the QA binding site, impacting the isotope edited FTIR difference spectra, crucial for understanding energy conversion processes in photosynthesis (Zhao et al., 2013).
- Duroquinone as a Molecular Ion Source: Research demonstrated the generation of molecular negative ions by Duroquinone, showcasing its potential in mass spectrometry applications for studying molecular ionization and longevity (Khvostenko et al., 2012).
- Duroquinone in Biochemical Sensors: Investigation into the optimization of gold electrode surfaces with photosystem II monolayers revealed Duroquinone′s critical role in enhancing sensor responses, applicable in biochemical sensor technology (Maly et al., 2005).
- Cytotoxicity of Duroquinone Congeners: A comparative study of 14 p-benzoquinone congeners, including Duroquinone, used quantitative structure-toxicity relationships to evaluate cytotoxicity in rat hepatocytes and PC12 cells, relevant for safety assessments in chemical manufacturing (Siraki et al., 2004).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Marilyn P Merker et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 290(3), L607-L619 (2005-10-26)
The objective of this study was to examine the impact of chronic hyperoxic exposure (95% O2 for 48 h) on intact bovine pulmonary arterial endothelial cell redox metabolism of 2,3,5,6-tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone (duroquinone, DQ). DQ or durohydroquinone (DQH2) was added to normoxic
Bingsheng Zhou et al.
Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 77(2), 136-142 (2006-01-18)
Toxicity of many waterborne organic contaminants to aquatic organisms is mediated through oxidative damages resulting from the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Using duroquinone as a model ROS inducer, we carried out in vitro and in vivo experiments to
Said H Audi et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 289(5), L788-L797 (2005-07-05)
NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) plays a dominant role in the reduction of the quinone compound 2,3,5,6-tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone (duroquinone, DQ) to durohydroquinone (DQH2) on passage through the rat lung. Exposure of adult rats to 85% O2 for > or =7 days stimulates
Xiao-Hui Duan et al.
The Journal of chemical physics, 120(21), 10025-10032 (2004-07-23)
Photoinduced electron transfer of the model system composed of vitamin E and duroquinone has been investigated using time-dependent density functional theory. Calculations for the excited states tell that the photoexcitation of the model system can directly yield the charge transfer
J Maly et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 381(8), 1558-1567 (2005-04-12)
Mass transport of the bulk of the analyte to the electrode and through the bioactive layer can be significantly improved by use of the nanoelectrode array and defined arrangement of protein film. This phenomenon has been studied by (i) atomic-force
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service