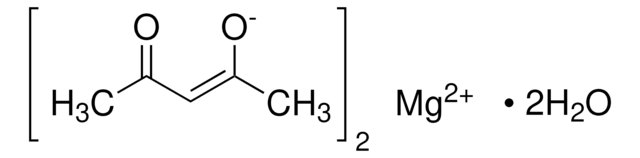
749044
Titanium
sputtering target, diam. × thickness 3.00 in. × 0.125 in., 99.995% trace metals basis
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
99.995% trace metals basis
form
solid
autoignition temp.
860 °F
reaction suitability
core: titanium
resistivity
42.0 μΩ-cm, 20°C
diam. × thickness
3.00 in. × 0.125 in.
bp
3287 °C (lit.)
mp
1660 °C (lit.)
density
4.5 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
[Ti]
InChI
1S/Ti
InChI key
RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Nanocomposite Coatings with Tunable Properties Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a data storage device that stores digital information by magnetizing nanosized magnets on flat disks and retrieves data by sensing the resulting magnetic field.
Spin-based electronic (spintronic) devices offer significant improvement to the limits of conventional charge-based memory and logic devices which suffer from high power usage, leakage current, performance saturation, and device complexity.
Can there be an effective strategy for finding breakthrough materials, since they are, by definition, unpredictable? One answer is found in Combinatorial Materials Science techniques, which represent a powerful approach to identifying new and unexpected materials.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service