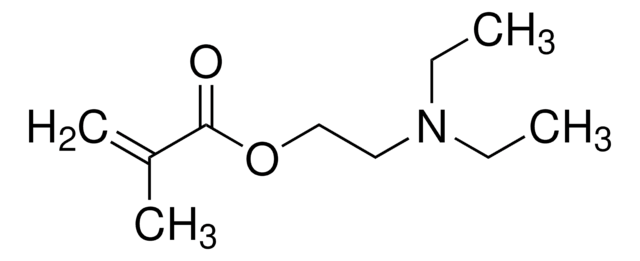
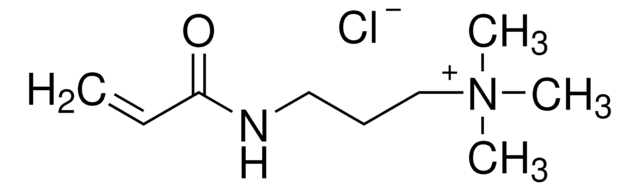
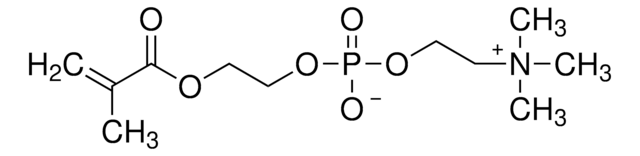
731099
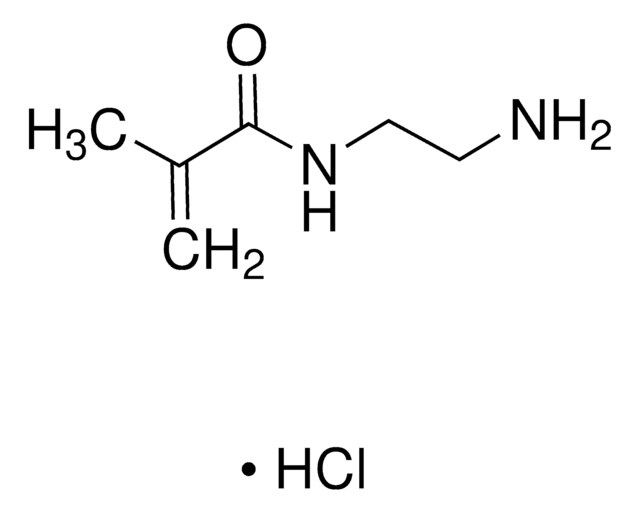
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride
contains ≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer, 98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
APMA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C7H14N2O · HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
178.66
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Assay
98% (HPLC)
form
powder
contains
≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer
mp
123-128 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
Cl.CC(=C)C(=O)NCCCN
InChI
1S/C7H14N2O.ClH/c1-6(2)7(10)9-5-3-4-8;/h1,3-5,8H2,2H3,(H,9,10);1H
InChI key
XHIRWEVPYCTARV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride (APMA) is an aminoalkyl methacrylamide which can be synthesized by adding 1,3-diaminopropane to 1,3-diaminopropane dihydrogen chloride solution and further mixing the solution with methacrylic anhydride and hydroquinone. It has a primary amine that provides attractive features such as pH-responsiveness, affinity for anionic drugs and conjugation for variety of chemical structures.
Application
APMA can be used in the preparation of copolymers and cross-linked miscellas for gene delivery, drug delivery and diagnostics applications.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Efficient RAFT polymerization of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylamide hydrochloride using unprotected ?clickable? chain transfer agents
Mendoncca PV, et al.
Reactive and Functional Polymers, 81(2), 1-7 (2014)
Facile synthesis of controlled-structure primary amine-based methacrylamide polymers via the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process
Deng Z, et al.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 46(15), 4984-4996 (2008)
Gaurasundar M Conley et al.
Nature communications, 10(1), 2436-2436 (2019-06-06)
Thermosensitive microgels are widely studied hybrid systems combining properties of polymers and colloidal particles in a unique way. Due to their complex morphology, their interactions and packing, and consequentially the viscoelasticity of suspensions made from microgels, are still not fully
Polymer mediated peptide immobilization onto amino-containing N-isopropylacrylamide-styrene core-shell particles
Rossi S, et al.
Colloid and Polymer Science, 282(3), 215-222 (2004)
Michika Onoda et al.
Nature communications, 8, 15862-15862 (2017-07-14)
In the field of polymer science, many kinds of polymeric material systems that show a sol-gel transition have been created. However, most systems are unidirectional stimuli-responsive systems that require physical signals such as a change in temperature. Here, we report
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service



![N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamide 99%, contains MEHQ as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/295/145/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951/640/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951.png)

![[3-(Methacryloylamino)propyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 50 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/189/736/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828/640/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828.png)