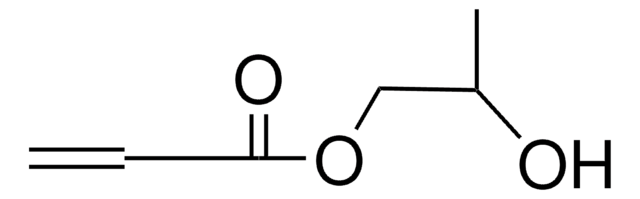
552348
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate
contains 900-1100 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
β-(Acryloyloxy)propionic acid, β-Carboxyethyl acrylate, 3-(Acryloyloxy)propionic acid, 3-Acryloyloxypropanoic acid, Acrylic acid 2-carboxyethyl ester, Acrylic acid dimer
About This Item
Recommended Products
contains
900-1100 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Quality Level
refractive index
n20/D 1.457 (lit.)
pH
2.95 (10 wt. % in H2O)
bp
103 °C/19 mmHg (lit.)
solubility
H2O: soluble
density
1.214 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OC(=O)CCOC(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C6H8O4/c1-2-6(9)10-4-3-5(7)8/h2H,1,3-4H2,(H,7,8)
InChI key
CYUZOYPRAQASLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
Application
Features and Benefits
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
110 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service




![Bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/128/336/4e7a3e38-338c-423e-95b8-70d9d1f8e121/640/4e7a3e38-338c-423e-95b8-70d9d1f8e121.png)