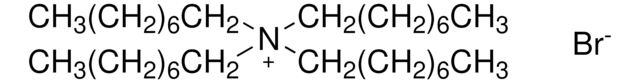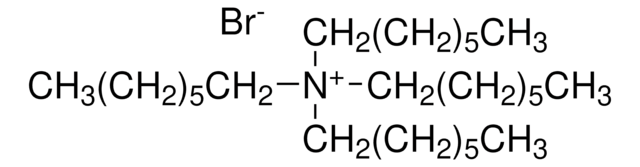All Photos(2)
About This Item
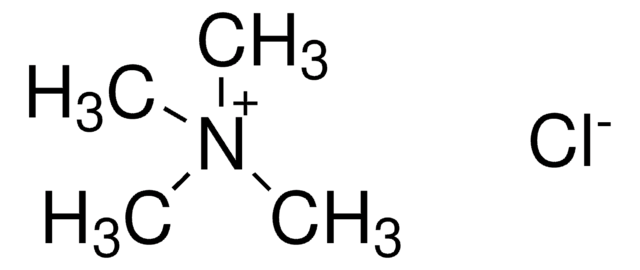
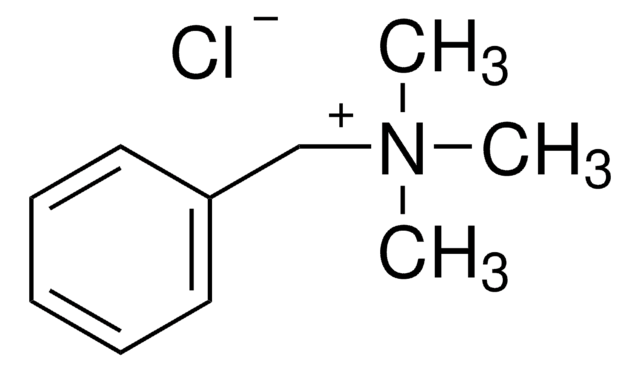
Linear Formula:
[CH3(CH2)4]4N(Cl)
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
334.02
Beilstein:
3573674
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352116
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
vapor density
11.5 (vs air)
Assay
99%
form
solid
SMILES string
[Cl-].CCCCC[N+](CCCCC)(CCCCC)CCCCC
InChI
1S/C20H44N.ClH/c1-5-9-13-17-21(18-14-10-6-2,19-15-11-7-3)20-16-12-8-4;/h5-20H2,1-4H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
SXAWRMKQZKPHNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Xiaoqing Hua et al.
Soft matter, 14(19), 3818-3828 (2018-05-03)
Understanding the dynamic adsorption of nanoparticles (NPs) at fluid interfaces is important for stabilizing emulsions and for the preparation of 2D NP-based materials. Here we show that the Ward-Tordai equations commonly employed to describe the dynamics of surfactant adsorption at
Xiaoqing Hua et al.
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, 34(16), 4830-4842 (2018-04-11)
Nanoparticles (NPs) can add functionality (e.g., catalytic, optical, rheological) to an oil-water interface. Adsorption of ∼10 nm NPs can be reversible; however, the mechanisms for adsorption and its effects on surface pressure remain poorly understood. Here we demonstrate how the
Rebecca S Lam et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1667(2), 241-248 (2004-12-08)
Changes in the level of membrane cholesterol regulate a variety of signaling processes including those mediated by acylated signaling molecules that localize to lipid rafts. Recently several types of ion channels have been shown to have cholesterol-dependent activity and to
Katsuya Dezaki et al.
Apoptosis : an international journal on programmed cell death, 17(8), 821-831 (2012-03-31)
Sustained rise in cytosolic Ca(2+) and cell shrinkage mainly caused by K(+) and Cl(-) efflux are known to be prerequisites to apoptotic cell death. Here, we investigated how the efflux of K(+) and Cl(-) as well as the rise in
B Unsöld et al.
Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology, 441(2-3), 368-378 (2001-02-24)
Previous studies have shown that heteromultimeric KCNQ1/KCNE1 (KvLQT1/minK) channels and homomultimeric KCNQ1 (KvLQT1) channels exhibit different current properties, e.g. distinct kinetics and different sensitivities to drugs. In this study we report on the divergent responses to internal pH changes and
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service