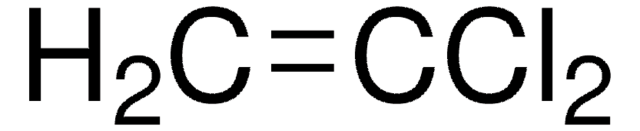163023
1,1-Dichloroethylene
contains 200 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99%
Synonym(s):
Vinylidene chloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
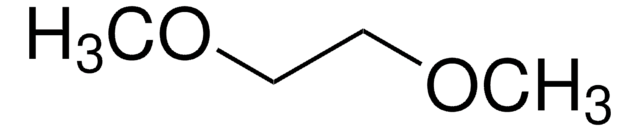
Linear Formula:
CH2=CCl2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
96.94
Beilstein:
1733365
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
vapor density
3.46 (vs air)
vapor pressure
9.68 psi ( 20 °C)
Assay
99%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
968 °F
contains
200 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
expl. lim.
15.5 %
bp
30-32 °C (lit.)
mp
−122 °C (lit.)
density
1.213 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
ClC(Cl)=C
InChI
1S/C2H2Cl2/c1-2(3)4/h1H2
InChI key
LGXVIGDEPROXKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
1,1-Dichloroethylene can be used as a monomer to synthesize polymercomposite latexes by emulsion polymerization.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
-2.2 °F
Flash Point(C)
-19 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Fan Chen et al.
Frontiers in microbiology, 9, 2306-2306 (2018-10-17)
Bioelectrochemical systems (BESs) are regarded as a promising approach for the enhanced dechlorination of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons (CAHs). However, the electron distribution and transfer considering dechlorination, methanogenesis, and other bioprocesses in these systems are little understood. This study investigated the
Xin Ma et al.
Water research, 40(6), 1155-1166 (2006-02-28)
Column experiments were performed to investigate a technology for remediating aquifers contaminated with chlorinated solvents. The technology involves installation of hollow-fiber membranes in the subsurface to supply hydrogen gas (H2) to groundwater to support biological reductive dechlorination in situ. Three
Juliet A Jones et al.
Chemical research in toxicology, 16(10), 1306-1317 (2003-10-21)
A proteome profiling approach was used to compare effects of two toxicants, 1,1-dicloroethylene (DCE) and diclofenac, which covalently adduct hepatic proteins. Bile was examined as a potential source of protein alterations since both toxicants target the hepatic biliary canaliculus. Bile
Erik J Martin et al.
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics, 304(1), 121-129 (2002-12-20)
Hepatotoxicity induced by 1,1-dichloroethylene (DCE) is mediated by cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism to reactive intermediates, including the epoxide. We have tested the hypothesis that mitochondria are a primary target of toxicity by investigating dose- and time-dependent effects of DCE on mitochondrial
Masarin Ban et al.
Toxicology, 184(1), 41-50 (2002-12-31)
Using immunotoxic functional tests, namely IgM response to sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production, this study simultaneously evaluated the effects of inhaled chloroform (10, 20, and 50 ppm), carbon tetrachloride (100, 200, and 300 ppm), 1,1-dichloroethylene (5
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service