推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
IgG fraction of antiserum
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
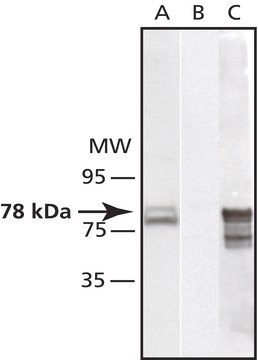
antigen 57 kDa
物種活性
mouse, bovine, rat, human
技術
immunoprecipitation (IP): 10-20 μg using RIPA lysate from rat NRK cells
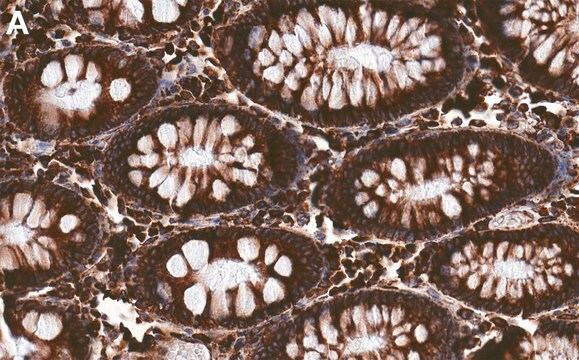
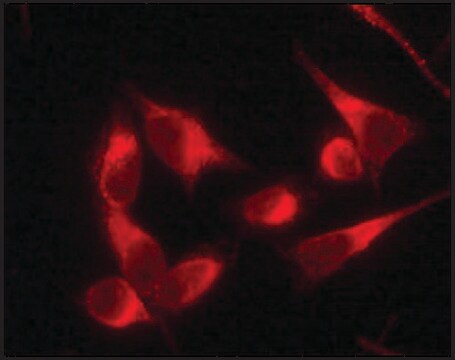
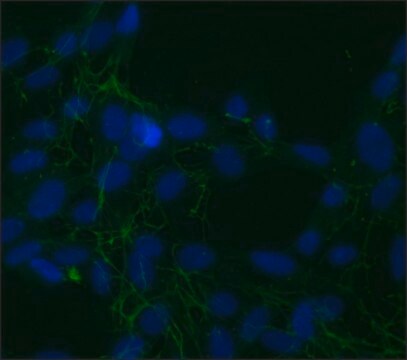
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:250 using human HeLa cells
western blot: 1:2,000 using whole extract of mouse NIH3T3 cells
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... P4HB(5034)
mouse ... P4hb(18453)
rat ... P4hb(25506)
一般說明
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit β (P4HB) or protein disulfide isomerase is a redox-regulated thiol-containing protein. The gene encoding this protein is localized on human chromosome 17q25.3.
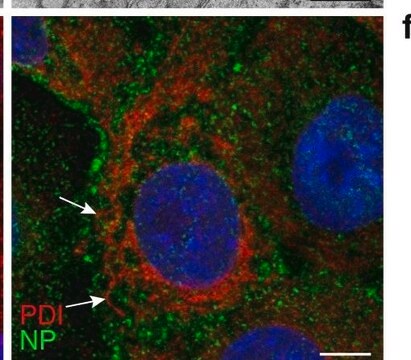
Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI, Erp58) is an abundant multifunctional, soluble enzyme (E.C. 5.3.4.1) that resides in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells. It consists of four tandem domains, two of which contain a catalytic site for disulfide bond formation. A mitochondrial isoform of PDI (approx. 54 kDa) has been recently described. PDI has an N-terminal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) signal and a C-terminal ER- retention KDEL signal sequences. PDI was found on the cell surface of several cell types including endothelial cells, platelets and hepatocytes.
免疫原
protein disulfide isomerase purified from bovine liver.
應用
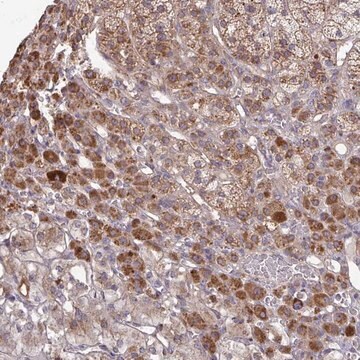
Anti-Protein Disulfide Isomerase antibody produced in rabbit has been used in immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence.
生化/生理作用
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit β (P4HB) or protein disulfide isomerase acts as a molecular chaperone in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells and also as an oxidoreductase. It associates with steroid hormones and modulates their actions, concentrations and storage. P4HB accelerates the formation of disulphide bonds in proteins and hence aids in their folding.
Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI) catalyzes the formation and rearrangements of both intrachain and interchain disulfide bonds in secreted proteins. It plays an important role in various cellular processes including cell adhesion. PDI has calcium-dependent transglutaminase activity and is involved in the catalysis of isopeptide bond formation. PDI participates in the hydroxylation of proline in procollagen during collagen synthesis and in the transfer of neutral lipid onto nascent lipoprotein particles. Estrogen binding by PDI has also been reported.
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
nwg
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
The Nuclear Pore Complex Function of Sec13 Protein Is Required for Cell Survival during Retinal Development*
Xubo Niu
The Journal of Biological Chemistry (2014)
Novel roles for protein disulphide isomerase in disease states: a double edged sword?
Parakh S and Atkin JD
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 3, 30-30 (2015)
Quantitative Transcriptomic Profiling of Branching in a
Glycosphingolipid Biosynthetic Pathway
Glycosphingolipid Biosynthetic Pathway
Hiromu Takematsu
The Journal of Biological Chemistry (2011)
Characterization of the estradiol-binding site structure of human protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
Fu XM, et al.
Testing, 6(11), e27185-e27185 (2011)
Hiromu Takematsu et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(31), 27214-27224 (2011-06-15)
Cellular biosynthesis of macromolecules often involves highly branched enzyme pathways, thus cellular regulation of such pathways could be rather difficult. To understand the regulatory mechanism, a systematic approach could be useful. We genetically analyzed a branched biosynthetic pathway for glycosphingolipid
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務