推薦產品
一般說明
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization technique (FISH) is based on the hybridization of fluorescent labeled oligonucleotide probe to a specific complementary DNA or RNA sequence in whole and intact cells.1 Microbial FISH allows the visualization, identification and isolation of bacteria due to recognition of ribosomal RNA also in unculturable samples.2
FISH technique can serve as a powerful tool in the microbiome research field by allowing the observation of native microbial populations in diverse microbiome environments, such as samples from human origin (blood3 and tissue4), microbial ecology (solid biofilms5 and aquatic systems 6) and plants 7. It is strongly recommended to include positive and negative controls in FISH assays to ensure specific binding of the probe of interest and appropriate protocol conditions. We offer positive (MBD0032/33) and negative (MBD0034/35) control probes, that accompany the specific probe of interest.
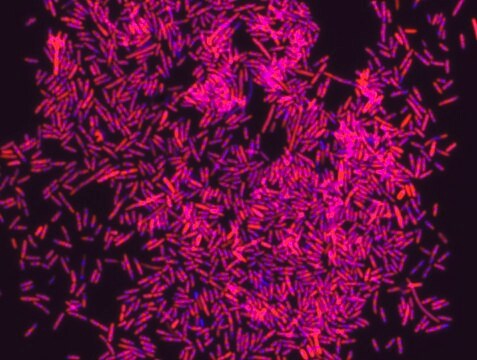
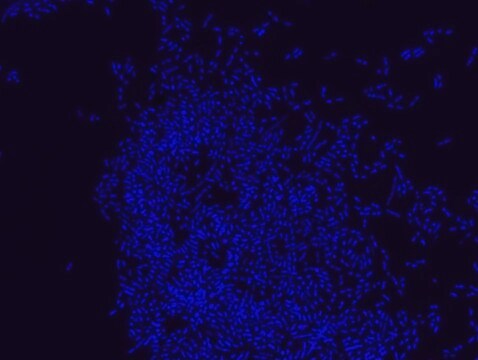
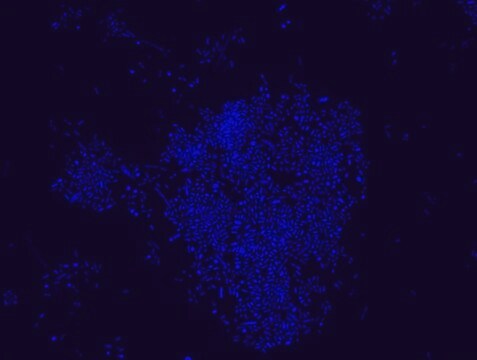
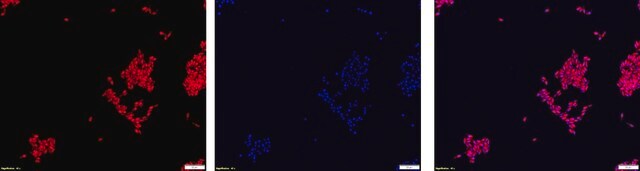
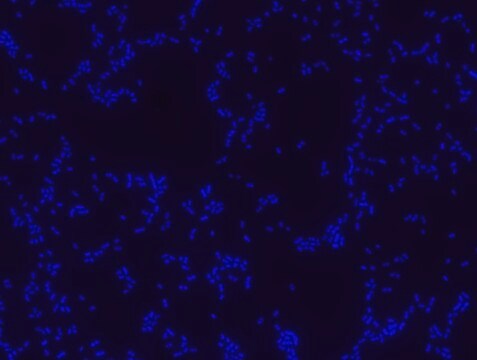
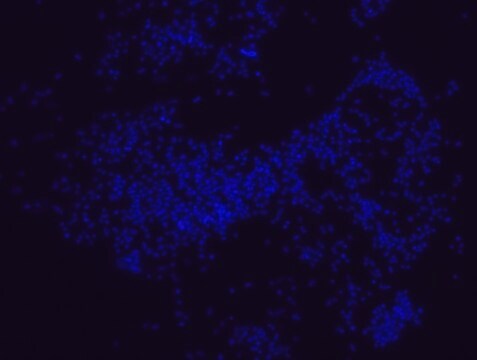
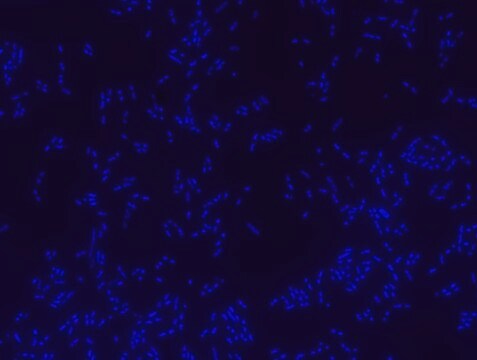
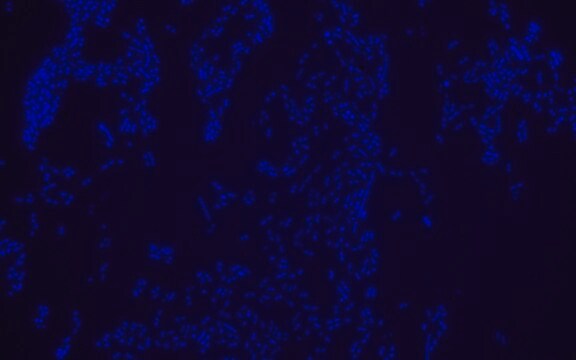
Proteus probe specifically recognizes Proteus species (see images of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis). Moreover, it was shown that this probe recognizes Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri.16
P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris are gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria. Bacteria of the genus Proteus (Proteus spp.) of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens, that often reside in the human intestine, and are responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.8,9 Proteus genus that includes P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri, are widespread in the environment and often serve as an indicator for soil or water fecal pollution.9
P. mirabilis causes up to 90% of all Proteus spp. infections and is more frequently associated with urinary tract infections then P. vulgaris.9 Proteus spp. have various virulence factors such as, fimbriae, flagella, enzymes (urease, proteases, and amino acid deaminases), and toxins (hemolysins and endotoxin).10
The most common infection involving P.mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.10 The immunological response against P. mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.11 A possible correlation between the abundance of
P.mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.12
P. vulgaris inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces.8 Moreover, it was also observed in fecal samples of healthy individuals.13
P. mirabilis has developed resistance to various classes of antibiotics, such as β-lactams aminoglycosides and tetracyclines.14 However, P. mirabilis strains are generally more susceptible to antimicrobials than are P. vulgaris,
P. penneri, and P. hauseri.15
FISH technique was successfully used for clinical detection of Proteus spp. in artificial urine medium and urine samples from patients with UTIs. The probe was able to detect 11 strains of P.mirabilis, 6 strains of P. vulgaris, 2 strains of P.penneri and one strain of P. hauseri.16 The probe can also be used to detect P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris pure culture (as described in the figure legends). FISH can also be implicated to detect Proteus spp. in colon sections embedded in paraffin.17,18 Moreover, FISH can be implicated to identify Proteus spp. in the gut of the medicinal leech.19
FISH technique can serve as a powerful tool in the microbiome research field by allowing the observation of native microbial populations in diverse microbiome environments, such as samples from human origin (blood3 and tissue4), microbial ecology (solid biofilms5 and aquatic systems 6) and plants 7. It is strongly recommended to include positive and negative controls in FISH assays to ensure specific binding of the probe of interest and appropriate protocol conditions. We offer positive (MBD0032/33) and negative (MBD0034/35) control probes, that accompany the specific probe of interest.
Proteus probe specifically recognizes Proteus species (see images of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis). Moreover, it was shown that this probe recognizes Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri.16
P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris are gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria. Bacteria of the genus Proteus (Proteus spp.) of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens, that often reside in the human intestine, and are responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.8,9 Proteus genus that includes P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri, are widespread in the environment and often serve as an indicator for soil or water fecal pollution.9
P. mirabilis causes up to 90% of all Proteus spp. infections and is more frequently associated with urinary tract infections then P. vulgaris.9 Proteus spp. have various virulence factors such as, fimbriae, flagella, enzymes (urease, proteases, and amino acid deaminases), and toxins (hemolysins and endotoxin).10
The most common infection involving P.mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.10 The immunological response against P. mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.11 A possible correlation between the abundance of
P.mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.12
P. vulgaris inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces.8 Moreover, it was also observed in fecal samples of healthy individuals.13
P. mirabilis has developed resistance to various classes of antibiotics, such as β-lactams aminoglycosides and tetracyclines.14 However, P. mirabilis strains are generally more susceptible to antimicrobials than are P. vulgaris,
P. penneri, and P. hauseri.15
FISH technique was successfully used for clinical detection of Proteus spp. in artificial urine medium and urine samples from patients with UTIs. The probe was able to detect 11 strains of P.mirabilis, 6 strains of P. vulgaris, 2 strains of P.penneri and one strain of P. hauseri.16 The probe can also be used to detect P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris pure culture (as described in the figure legends). FISH can also be implicated to detect Proteus spp. in colon sections embedded in paraffin.17,18 Moreover, FISH can be implicated to identify Proteus spp. in the gut of the medicinal leech.19
應用
Probe for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH),recognizes Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis cells.
特點和優勢
- Visualize, identify and isolate Proteus spp. cells.
- Observe native Proteus spp. cell populations in diverse microbiome environments.
- Specific, sensitive and robust identification of Proteus spp. in bacterial mixed population.
- Specific, sensitive and robust identification even when Proteus spp. are in low abundance in the sample.
- FISH can complete PCR based detection methods by avoiding contaminant bacteria detection.
- Provides information on Proteus spp. morphology and allows to study biofilm architecture.
- Identify Proteus spp. in clinical samples such as, urine samples and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples.
- The ability to detect Proteus spp. in its natural habitat is an essential tool for studying host-microbiome interaction.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
nwg
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Nerea Porres-Osante et al.
Microbial ecology, 70(1), 132-140 (2014-12-17)
The intestinal tract is a huge reservoir of Enterobacteriaceae, some of which are opportunist pathogens. Several genera of these bacteria harbour intrinsic antibiotic resistance genes, such as ampC genes in species of Citrobacter, Enterobacter or Escherichia genera. In this work
Michele A Maltz et al.
Frontiers in microbiology, 5, 151-151 (2014-05-27)
There are trillions of microbes found throughout the human body and they exceed the number of eukaryotic cells by 10-fold. Metagenomic studies have revealed that the majority of these microbes are found within the gut, playing an important role in
Ryu Okumura et al.
Nature, 532(7597), 117-121 (2016-03-31)
Colonic epithelial cells are covered by thick inner and outer mucus layers. The inner mucus layer is free of commensal microbiota, which contributes to the maintenance of gut homeostasis. In the small intestine, molecules critical for prevention of bacterial invasion
Michal Arabski et al.
Clinical biochemistry, 45(16-17), 1374-1382 (2012-07-04)
Proteus mirabilis strains are human pathogens responsible for urinary tract infections, which may also be involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We determined whether the binding site of anti-LPS antibodies on the O-polysaccharide part of P. mirabilis LPS correlates with the
A Rózalski et al.
Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR, 61(1), 65-89 (1997-03-01)
The object of this review is the genus Proteus, which contains bacteria considered now to belong to the opportunistic pathogens. Widely distributed in nature (in soil, water, and sewage), Proteus species play a significant ecological role. When present in the
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務