推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~150 kDa
物種活性
rat, canine
技術
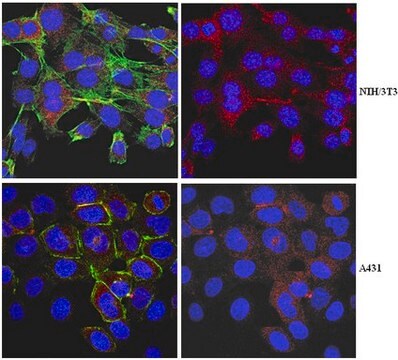
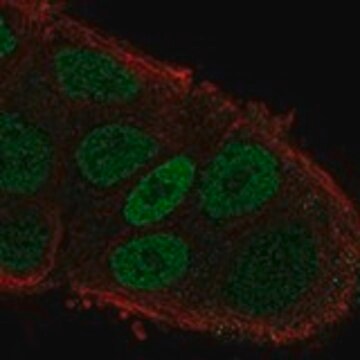
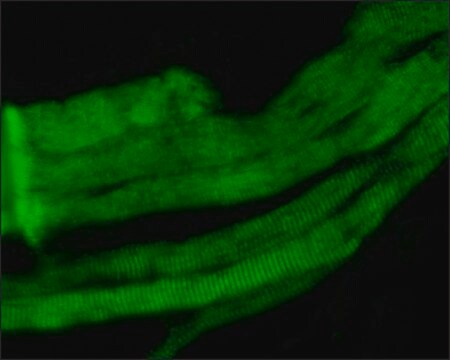
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:75 using cultured rat NRK cells
microarray: suitable
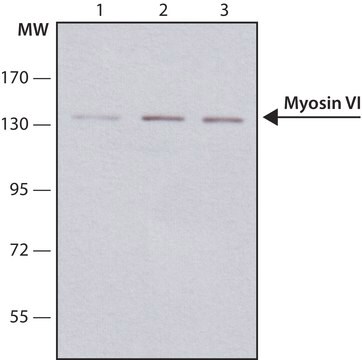
western blot: 1:1,000 using a whole extract of cultured dog MDCK cells
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... MYO6(4646)
一般說明
Myosin VI (MYO6) is localized to the Golgi complex and is expressed in the hair cells of the ear. It is a two-headed myosin with a short coiled-coil segment in its tail. The motor domain of MYO6 has two insertions. The gene encoding this protein is localized on chromosome 6q13.
Myosin VI is a relatively abundant widespread unconventional myosin composed of an N-terminal motor domain, a light chain binding neck region, a coiled-coiled region, and a highly conserved C-terminal domain. At the ′converter′ region, between the catalytic head and the neck region of Myosin VI, there is a characteristic linker about 50 amino acids long. Native Myosin VI is apparently a two-headed dimer of the heavy chains with each heavy chain bound to calmodulin light chain.
免疫原
synthetic peptide corresponding to an epitope within the C-terminal of human Myosin VI, with N-terminal cysteine added, conjugated to KLH.
應用
Anti-Myosin VI (KA-15) antibody has been used:
- in immunoblotting
- in immunocytochemistry
- in immunofluorescence
- immunohistochemistry
- proximity ligation assay
生化/生理作用
Myosin VI participates in the generation of cell shape change, cell motility, membrane remodeling, and possibly in organelle and particle transport or tethering. It is also involved in membrane trafficking pathways in cultured mammalian cells where it is associated with the membrane ruffles and the trans-Golgi network. The unusual direction of Myosin VI movement may suggest that it brings materials or membranes into the cell. Its activity in tissue cultured cells is thought to be regulated by phosphorylation. A mutation in Myosin VI was described recently in human autosomal dominant non syndromic hearing loss.
外觀
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% BSA and 15 mM sodium azide.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Stepwise movements in vesicle transport of HER2 by motor proteins in living cells
Watanabe T M and Higuchi H
Biophysical Journal, 92(11), 4109-4120 (2007)
Myosin VI: two distinct roles in endocytosis
Hasson T.
Journal of Cell Science, 116(17), 3453-3461 (2003)
Katrina M Schrode et al.
eNeuro, 5(4) (2018-08-21)
Noise exposure is one of the most common causes of hearing loss and peripheral damage to the auditory system. A growing literature suggests that the auditory system can compensate for peripheral loss through increased central neural activity. The current study
Maiko Miyagawa et al.
The Annals of otology, rhinology, and laryngology, 124 Suppl 1, 148S-157S (2015-05-23)
To elucidate the involvement of MYO6 mutations, known to be responsible for DFNA22/DFNB37, in Japanese hearing loss patients through the use of genetic analysis. Genomic variations responsible for hearing loss were identified by massively parallel DNA sequencing (MPS) of 63
Kali Burke et al.
eNeuro, 9(3) (2022-05-26)
Aging leads to degeneration of the peripheral and central auditory systems, hearing loss, and difficulty understanding sounds in noise. Aging is also associated with changes in susceptibility to or recovery from damaging noise exposures, although the effects of the interaction
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務