推薦產品
種類
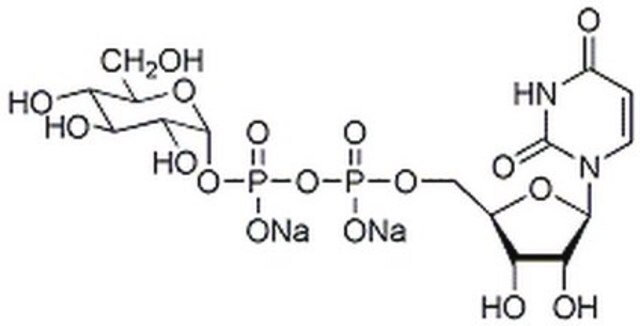
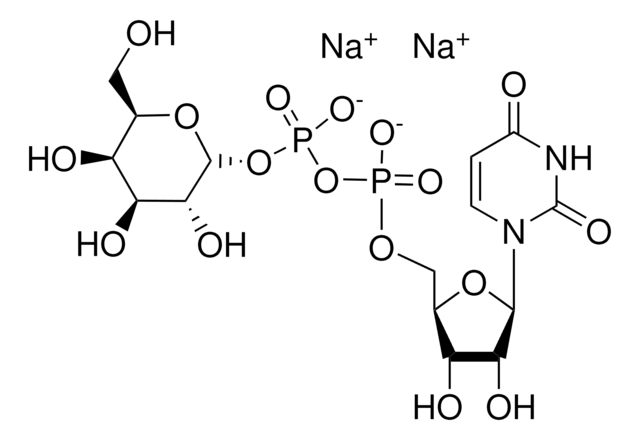
Type I
品質等級
化驗
≥97% (HPLC)
儲存溫度
−20°C
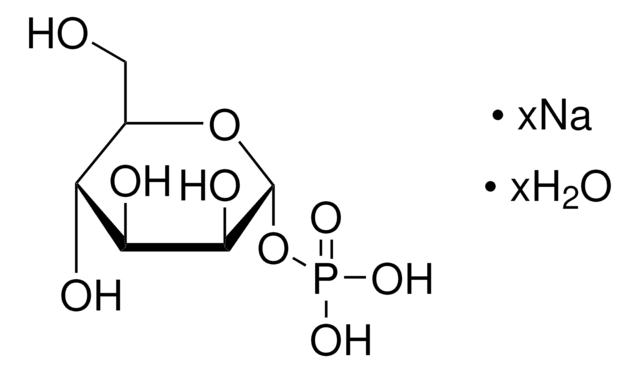
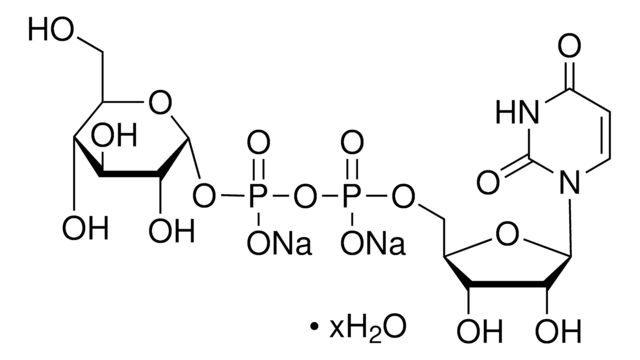
SMILES 字串
[Na].NC1=NC(=O)c2ncn(C3OC(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC4OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C4O)C(O)C3O)c2N1
InChI
1S/C16H25N5O16P2.Na.H/c17-16-19-12-6(13(28)20-16)18-3-21(12)14-10(26)8(24)5(34-14)2-33-38(29,30)37-39(31,32)36-15-11(27)9(25)7(23)4(1-22)35-15;;/h3-5,7-11,14-15,22-27H,1-2H2,(H,29,30)(H,31,32)(H3,17,19,20,28);;
InChI 密鑰
MEXITZOHWLXZKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
生化/生理作用
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
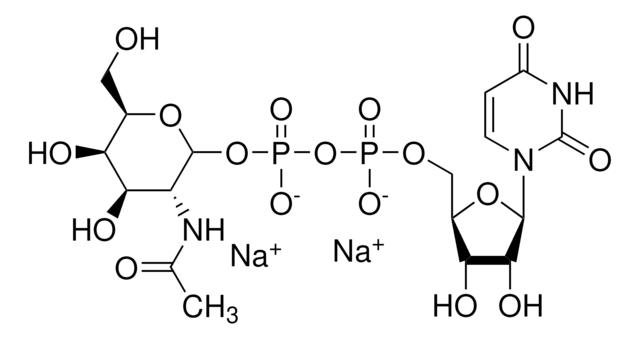
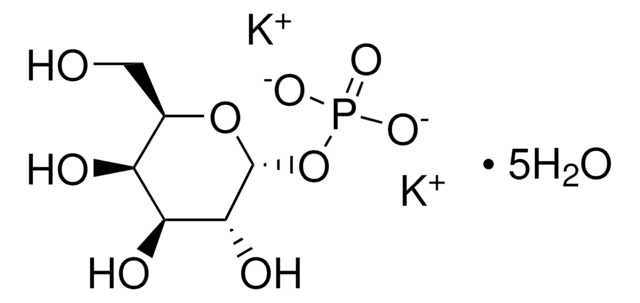
客戶也查看了
文章
The presence of multiple functional groups and stereocenters in complex carbohydrates makes them challenging targets for the organic chemist.
Glycosyltransferases were initially considered to be specific for a single glycosyl donor and acceptor, which led to the one enzyme-one linkage concept. Subsequent observations have refuted the theory of absolute enzymatic specificity by describing the transfer of analogs of some nucleoside mono- or diphosphate sugar donors.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務