推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~160 kDa
物種活性
mouse, human, rat
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
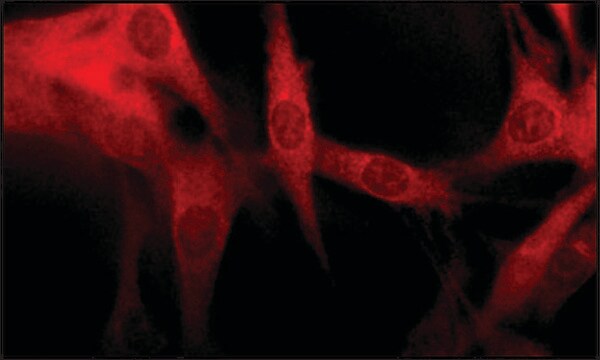
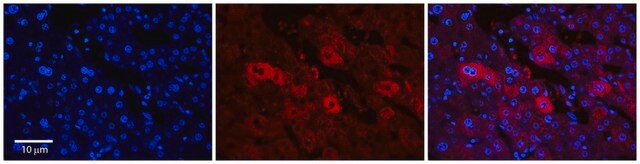
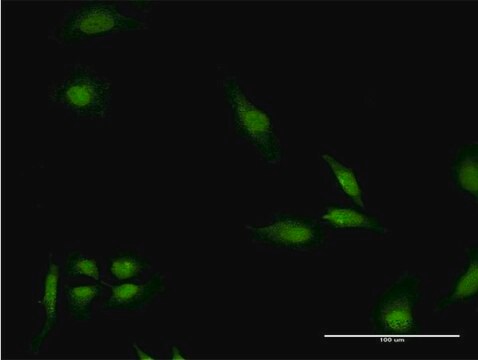
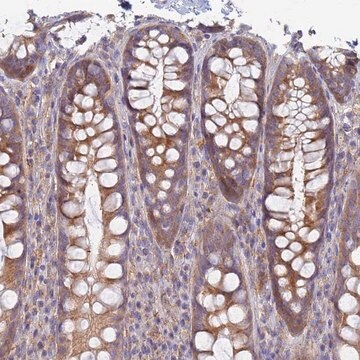
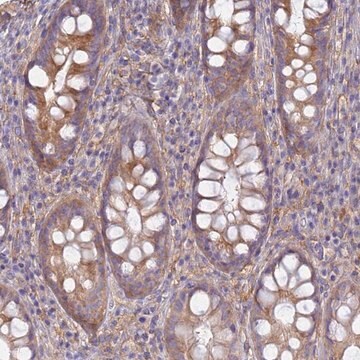
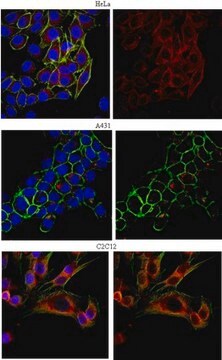
indirect immunofluorescence: 5-10 μg/mL using human HeLa and rat NRK cells
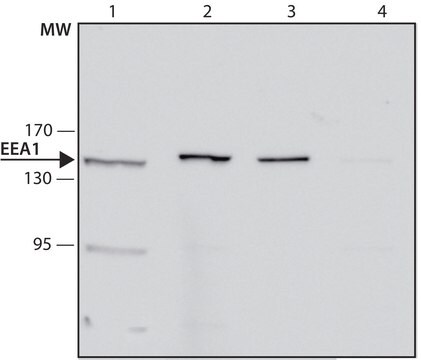
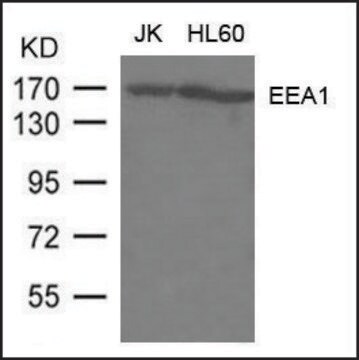
western blot (chemiluminescent): 0.4-0.8 μg/mL using whole extract of mouse NIH-3T3 cells
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... EEA1(8411)
mouse ... Eea1(216238)
rat ... Eea1(314764)
一般說明
The gene Early Endosome Antigen 1 (EEA1) encodes for around 1400 amino acid proteins. It is a peripheral membrane protein associated with the cytoplasmic face of early endosomes. It is a 162 kDa autoantigen protein. EEA1 is a dimer, which comprises extensive coiled-coil regions. At its C-terminus, it contains a cysteine-rich zinc-finger-like domain named FYVE domain. This FYVE domain is conserved from yeast to man. FYVE domain is implicated in the specific localization of EEA1 to endosomes.
免疫原
synthetic peptide corresponding amino acid residues 24-40 of human EEA1 with C-terminal added cysteine, conjugated to KLH. The corresponding sequence is identical in mouse.
應用
Anti-Early Endosomal Antigen 1 (N-terminal) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in immunoblotting and immunofluorescence.
生化/生理作用
Early Endosomal Antigen 1 (EEA1) localization in endosomes is implicated in subacute systemic lupus erythematosus. Endosomal targeting of EEA1 also requires its binding to the active form of the small GTPase Rab5. The binding of EEA1 to phosphatidylinositol 3 phosphate (PtdInsP) and rabaptin-5 (Rab5)-GTP is essential for the localization and function of EEA1 in endocytic membrane fusion. Anti-EEA1 may be used as an early endosome marker.
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Andree Hubber et al.
Scientific reports, 7, 44795-44795 (2017-03-21)
The evolutionarily conserved processes of endosome-lysosome maturation and macroautophagy are established mechanisms that limit survival of intracellular bacteria. Similarly, another emerging mechanism is LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP). Here we report that an intracellular vacuolar pathogen, Legionella dumoffii, is specifically targeted by
EEA1, a tethering protein of the early sorting endosome, shows a polarized distribution in hippocampal neurons, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts
Wilson JM, et al.
Molecular Biology of the Cell, 11(8), 2657-2671 (2000)
Jan Schulze-Luehrmann et al.
Cellular microbiology, 18(2), 181-194 (2015-08-08)
The obligate intracellular pathogen Coxiella burnetii replicates in a large phagolysosomal-like vacuole. Currently, both host and bacterial factors required for creating this replicative parasitophorous C. burnetii-containing vacuole (PV) are poorly defined. Here, we assessed the contributions of the most abundant
FYVE and coiled-coil domains determine the specific localisation of Hrs to early endosomes
Raiborg C, et al.
Journal of Cell Science, 114(12), 2255-2263 (2001)
Ziying Fu et al.
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 12, 71-71 (2018-04-05)
The main olfactory epithelium (MOE) functions to detect odor molecules, provide an epithelial surface barrier, and remove xenobiotics from inhaled air. Mechanisms coordinating the activities of different cell types within the MOE to maintain these functions are poorly understood. Previously
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務