推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
PBS solution
分子量
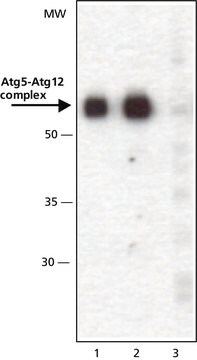
antigen ~56 kDa (Atg5-Atg12 complex)
物種活性
mouse, human, rat
包裝
antibody small pack of 25 μL
技術
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: 0.5-1 μg/mL using whole extracts of human K562, rat NRK, and mouse 3T3 cells
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... ATG5(9474)
mouse ... Atg5(11793)
rat ... Atg5(365601)
特異性
兔抗ATG5(N末端)可识别人、大鼠和小鼠的Atg5-Atg12复合物。
免疫原
对应于人ATG5第2-15个氨基酸的合成肽,通过C-末端的半胱氨酸残基与KLH发生偶联。相应的序列在大鼠和小鼠中是相同的。
應用
兔抗-ATG5抗体已用于免疫荧光和化学发光蛋白质印迹分析。
兔抗ATG5(N-末端特异性)用于蛋白质印迹分析,以检测通过表达 ATG5 特异性 shRNA 的腺病毒转导后,SK-N-MC 细胞中的 ATG5 水平。
成功使用该抗体的应用以及相关的同行评审论文如下所示。
蛋白质免疫印迹分析(1篇论文)
蛋白质免疫印迹分析(1篇论文)
抗 ATG5(N-末端)抗体已被用于:
- 免疫印迹
- 免疫荧光
- 蛋白质印迹
生化/生理作用
Atg5(Apg5)是一种自噬所需的32 kDa蛋白。Atg5由泛素样修饰剂Atg12共价修饰。由此形成的Atg12-Atg5-Atg16复合物栓系自噬体前体,并调节自噬体的形成。研究报告称通过钙蛋白酶裂解形成的Atg5片段具有促凋亡特性。
外觀
0.01 M 磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.4,含有 15 mM 叠氮化钠)溶液
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、体外或体内治疗用途,或人类或动物任何类型的消费或使用。
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
客戶也查看了
The deubiquitinating enzyme USP36 controls selective autophagy activation by ubiquitinated proteins.
Emmanuel Taillebourg et al.
Autophagy, 8(5), 767-779 (2012-05-25)
Initially described as a nonspecific degradation process induced upon starvation, autophagy is now known also to be involved in the degradation of specific ubiquitinated substrates such as mitochondria, bacteria and aggregated proteins, ensuring crucial functions in cell physiology and immunity.
Shintaro Seto et al.
PloS one, 8(12), e86017-e86017 (2014-01-01)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an intracellular pathogen that can survive within phagocytic cells by inhibiting phagolysosome biogenesis. However, host cells can control the intracellular M. tuberculosis burden by the induction of autophagy. The mechanism of autophagosome formation to M. tuberculosis has
Kallikrein-8 inhibition attenuates Alzheimer's disease pathology in mice
Herring A, et al.
Alzheimers Dement., 12(12), 1273-1287 (2016)
Denitsa S Petkova et al.
Viruses, 9(5) (2017-05-23)
Autophagy is a potent cell autonomous defense mechanism that engages the lysosomal pathway to fight intracellular pathogens. Several autophagy receptors can recognize invading pathogens in order to target them towards autophagy for their degradation after the fusion of pathogen-containing autophagosomes
Autophagy adaptor protein p62/SQSTM1 and autophagy-related gene Atg5 mediate autophagosome formation in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in dendritic cells
Seto S, et al.
PLoS ONE, 8(12), e86017-e86017 (2013)
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務