推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
100
500
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
culture supernatant
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
SP133, monoclonal
描述
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use in Select Regions (See Chart)
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
物種活性
human
包裝
vial of 0.1 mL concentrate (350R-14)
vial of 0.5 mL concentrate (350R-15)
bottle of 1.0 mL predilute (350R-17)
vial of 1.0 mL concentrate (350R-16)
bottle of 7.0 mL predilute (350R-18)
製造商/商標名
Cell Marque™
技術
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:100-1:500
同型
IgG
控制
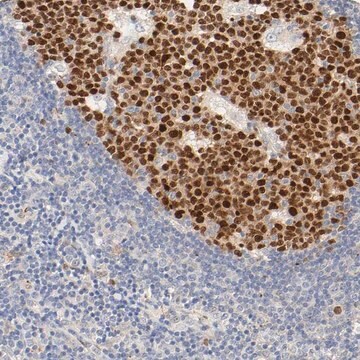
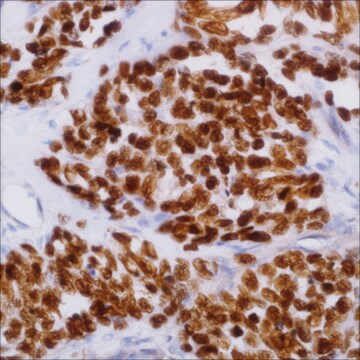
DLBCL, lymph node, tonsil
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
2-8°C
視覺化
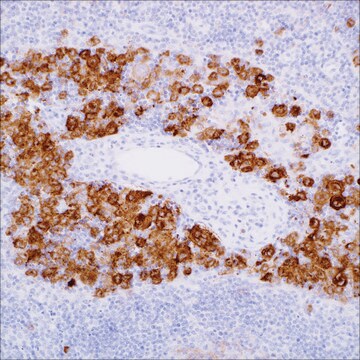
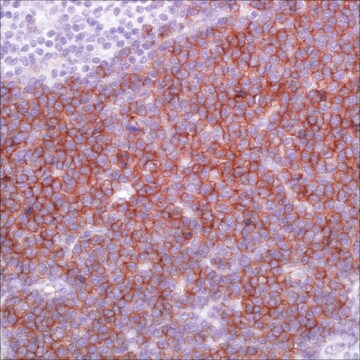
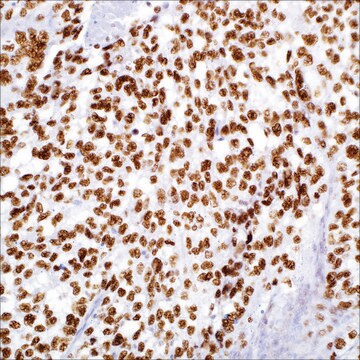
nuclear
基因資訊
human ... FOXP1(27086)
一般說明
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) represents different clinicopathologic entities which are difficult to separate using standard techniques. From the clinical standpoint, the introduction of immunochemotherapy in the treatment of DLBCL has dramatically improved the outcome of these patients compared with chemotherapy alone. Gene expression profiling (GEP) studies have shown that DLBCL can be reproducibly divided into the important subtypes of germinal center B-cell–like (GCB), activated B-cell–like (ABC), and unclassified DLBCL. It is beneficial to translate the GEP classification into protein expression by tumor cells through immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. A panel of antibodies: CD10, BCL6, MUM1/IRF4, GCET1, FoxP1, LMO2, and BCL2 has been used to determine GCB or ABC and each has different percentage thresholds for positive staining. Choi et al. demonstrated that the cases positive for GCET1 (≥ 80% of tumor cells) and MUM1/IRF4 (≥ 80%) and/or FoxP1 (≥ 80%) or negative for CD10 and BCL6 (≤ 30%) were assigned to the group. The cases positive for CD10 (≥ 30%), GCET1 (≥ 80%) without MUM1 expression, or positive for BCL6 without FoxP1 expression were classified as GCB. This study indicated the importance of FoxP1 in the subclassification of DLBCL. Choi et al then modified their approach to DLBCL subclassification by focusing on FoxP1. The tumors that are positive for both FoxP1 and GCET1 are assigned to GCB subgroup, but, if FoxP1 is positive and GCET1 is negative, the tumors belong to the ABC phenotype. If a case is FoxP1 negative but MUM-1/IRF4 positive, it still belongs to the ABC phenotype as long as CD10 is not expressed. This modified method emphasized the role of FoxP1, MUM1/IRF4, and GCET1 in the subclassification of DLBCL. The Choi′s algorithm had a very high concordance with the GEP results (87%). Therefore, FoxP1 is useful in subclassification of DLBCL and a high cutoff (≥80%) for FoxP1 is needed to achieve high specificity for the ABC subtype.
品質
 IVD |  IVD |  IVD |  RUO |
聯結
FoxP1 Positive Control Slides, Product No. 350S, are available for immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections).
外觀
Solution in Tris Buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, with 1% BSA and <0.1% Sodium Azide
準備報告
Download the IFU specific to your product lot and formatNote: This requires a keycode which can be found on your packaging or product label.
其他說明
For Technical Service please contact: 800-665-7284 or email: service@cellmarque.com
法律資訊
Cell Marque is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
Further studies on biosynthesis of erythropoietin.
R Bandyopadhyay et al.
Indian journal of biochemistry & biophysics, 18(4), 241-244 (1981-08-01)
Andreas Rosenwald et al.
The New England journal of medicine, 346(25), 1937-1947 (2002-06-21)
The survival of patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma after chemotherapy is influenced by molecular features of the tumors. We used the gene-expression profiles of these lymphomas to develop a molecular predictor of survival. Biopsy samples of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma from
Paul N Meyer et al.
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 29(2), 200-207 (2010-12-08)
Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) can be divided into prognostic groups based on the cell of origin of the tumor as determined by microarray analysis. Various immunohistochemical algorithms have been developed to replicate these microarray results and/or stratify
Swerdlow, SH et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008.
WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue (2008)
H Hagberg et al.
Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 17 Suppl 4, iv31-iv32 (2006-05-17)
The multicentre phase III CORAL study aims to guide choice of salvage chemotherapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and assess the role of rituximab maintenance after autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Patients are first randomised between ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務