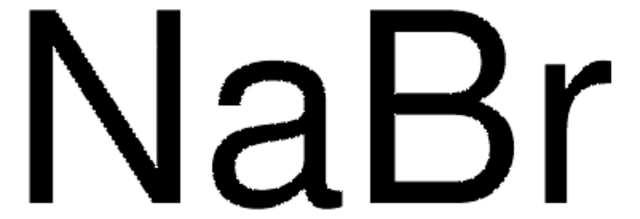推薦產品
等級
anhydrous
蒸汽壓力
1 mmHg ( 806 °C)
產品線
ReagentPlus®
Redi-Dri™
化驗
≥99%
形狀
powder
品質
free-flowing
pH值
5.4 (20 °C, 50 g/L)
mp
755 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
[Na+].[Br-]
InChI
1S/BrH.Na/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
InChI 密鑰
JHJLBTNAGRQEKS-UHFFFAOYSA-M
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
應用
法律資訊
ReagentPlus is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Redi-Dri is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Repr. 2 - STOT RE 2 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Central nervous system
儲存類別代碼
13 - Non Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
客戶也查看了
Patricia Cazón et al.
Carbohydrate polymers, 216, 72-85 (2019-05-03)
Bacterial cellulose (BC) produced by Komagataeibacter xylinus is a biomaterial with a unique three-dimensional structure. To improve the mechanical properties and reinforce the BC films, they were immersed in polyvinyl alcohol (0-4%) and chitosan (0-1%) baths. Moisture content, mechanical properties
Patricia Cazón et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 117, 235-246 (2018-05-25)
The aim of this study was to develop composite films from cellulose, chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol to obtain environmentally friendly materials. Toughness, burst strength, distance to burst and water adsorption properties were measured and analysed as a function of cellulose
Christian Freese et al.
Particle and fibre toxicology, 11, 68-68 (2014-12-30)
In general the prediction of the toxicity and therapeutic efficacy of engineered nanoparticles in humans is initially determined using in vitro static cell culture assays. However, such test systems may not be sufficient for testing nanoparticles intended for intravenous application.
Ramon Weishaupt et al.
Biomacromolecules, 16(11), 3640-3650 (2015-09-29)
Controlled and efficient immobilization of specific biomolecules is a key technology to introduce new, favorable functions to materials suitable for biomedical applications. Here, we describe an innovative and efficient, two-step methodology for the stable immobilization of various biomolecules, including small
Yi-Ling Hsieh et al.
Pharmaceutical research, 32(2), 549-561 (2014-08-26)
The aim of this study was to investigate how factors such as temperature, relative humidity and particle size impact the extent of disproportionation (salt to free base conversion) in powder blends of miconazole, benzocaine or sertraline mesylate salts mixed with
文章
Redi-Dri™ prevents hygroscopic powders, such as inorganic salts, from absorbing moisture and forming clumps, leaving the salts free-flowing every time.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務