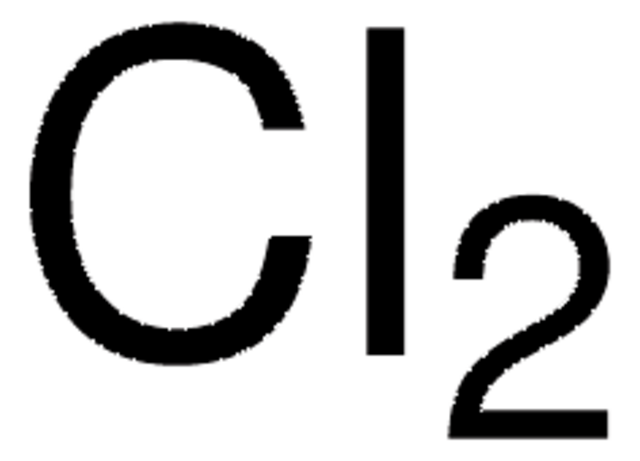推薦產品
蒸汽密度
2.48 (vs air)
蒸汽壓力
4800 mmHg ( 20 °C)
等級
puriss.
化驗
≥99.8%
電阻係數
1E9 μΩ-cm, 20°C
蒸發殘留物
≤40 ppm
bp
−34 °C (lit.)
mp
−101 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
ClCl
InChI
1S/Cl2/c1-2
InChI 密鑰
KZBUYRJDOAKODT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
包裝
罐装,净重 ~2kg
DIN 477 nr.8
分析報告
对应 DIN 19607"水处理用氯气"
其他說明
可能实行销售限制
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Aquatic Acute 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Ox. Gas 1 - Press. Gas Compr. Gas - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Respiratory system
儲存類別代碼
2A - Gases
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
客戶也查看了
Suhail Ahmad et al.
Environmental research, 133, 20-26 (2014-06-07)
Invasive aspergillosis due to triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus, a common airborne fungal pathogen, has emerged in some European and Asian countries, likely due to exposure to azole fungicides in the environment. This study determined the occurrence of triazole-resistant A. fumigatus in
Marie Deborde et al.
Water research, 42(1-2), 13-51 (2007-10-05)
Numerous inorganic and organic micropollutants can undergo reactions with chlorine. However, for certain compounds, the expected chlorine reactivity is low and only small modifications in the parent compound's structure are expected under typical water treatment conditions. To better understand/predict chlorine
Melissa A Gessner et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 304(11), L765-L773 (2013-04-09)
Chlorine (Cl₂) is a highly irritating and reactive gas with potential occupational and environmental hazards. Acute exposure to Cl₂ induces severe epithelial damage, airway hyperreactivity, impaired alveolar fluid clearance, and pulmonary edema in the presence of heightened inflammation and significant
G Rossi-Fedele et al.
International endodontic journal, 44(9), 792-799 (2011-06-11)
Chlorine-containing solutions are used for broad disinfection purposes. Water disinfection literature suggests that their disinfectant action depends on pH values as this will influence the available free chlorine forms. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has been suggested to have an antimicrobial effect
Per Bengtson et al.
Environmental microbiology, 11(6), 1330-1339 (2009-05-21)
Several studies have demonstrated that extensive formation of organically bound chlorine occurs both in soil and in decaying plant material. Previous studies suggest that enzymatic formation of reactive chlorine outside cells is a major source. However, the ecological role of
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務