推薦產品
product name
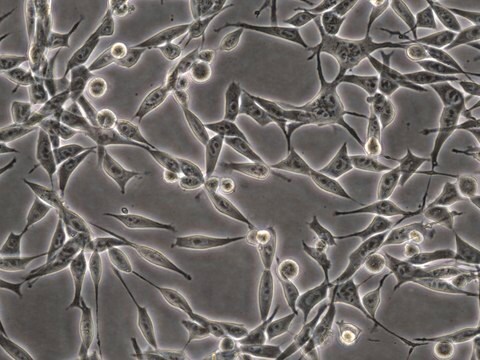
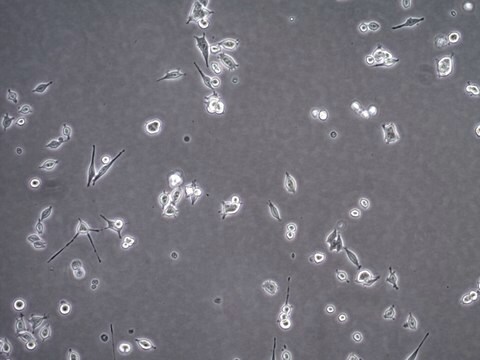
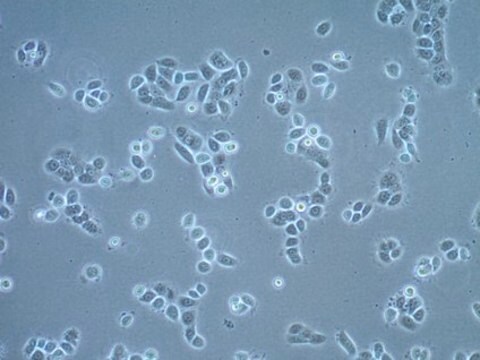
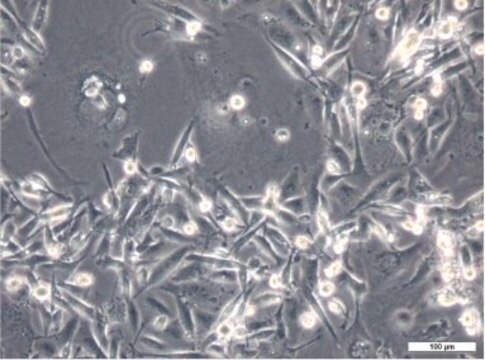
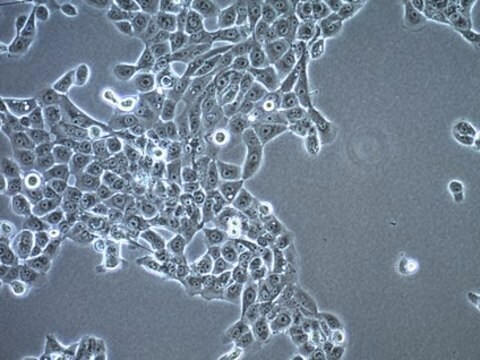
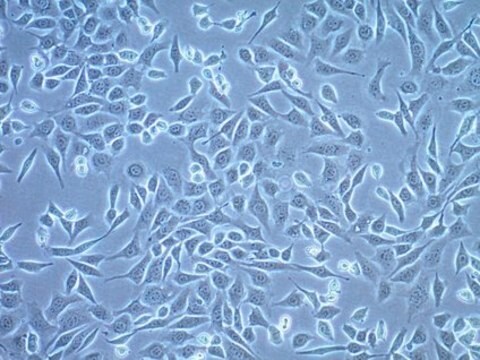
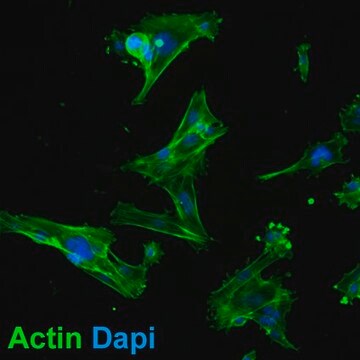
MB49小鼠膀胱癌细胞系, MB49 mouse urothelial carcinoma cell line is widely used as an in vitro and in vivo model of bladder cancer.
生物源
mouse
品質等級
技術
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
運輸包裝
ambient
一般說明
MB49细胞来自C57BL/Icrf-a’小鼠膀胱上皮细胞,在长期原代培养的第二天经化学致癌物7, 12-二甲苯[a]蒽(DMBA)单独处理24小时后转化。 经证实,移植到同基因鼠体内的转化细胞可诱发癌症。 而对父系起源,核型分析表明Y染色体在所分析的细胞中会100%丢失。 这种异常是人类膀胱癌的常见早期事件。 最近的一项研究表明,MB49细胞再现了膀胱肿瘤生长中性别差异的关键特征。 MB49植入小鼠后,雄性小鼠的肿瘤明显大于雌性小鼠。 在双氢睾酮的作用下,MB49细胞呈剂量依赖性增殖增强。 相反,MB49细胞对妊娠激素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素(hCG)无反应。MB49细胞表现为MHC-I类和II类分子的低表达或不表达。 然而,IFN-暴露后,MHC I类和II类表达显著上调。
品質
• 每小瓶含有≥ 1X106个活细胞。
• Charles River动物诊断服务通过小鼠Essential CLEAR小组对细胞进行传染病检测,结果为阴性。
• 通过Charles River动物诊断服务的污染透明小组评估,证实细胞为小鼠来源,对大鼠、中国仓鼠、金色黄叙利亚仓鼠、人和非人灵长类动物(NHP)的种间污染物呈阴性。
• 细胞对支原体污染呈阴性
• Charles River动物诊断服务通过小鼠Essential CLEAR小组对细胞进行传染病检测,结果为阴性。
• 通过Charles River动物诊断服务的污染透明小组评估,证实细胞为小鼠来源,对大鼠、中国仓鼠、金色黄叙利亚仓鼠、人和非人灵长类动物(NHP)的种间污染物呈阴性。
• 细胞对支原体污染呈阴性
其他說明
根据产品文件中详述的“学术使用协议”的条款,本产品预期仅用于销售和销售给学术机构,以供内部学术研究使用。有关任何其他用途的信息,请联系licensing@emdmillipore.com。
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
I C Summerhayes et al.
Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 62(4), 1017-1023 (1979-04-01)
Neoplastic transformation of C57BL/lcrf-a' mouse bladder epithelium was induced in long-term primary cultures by a single 24-hour treatment with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene on day 2 of culture. Transformed foci appeared earlier (40--60 days) and at a higher frequency (28%) in cultures from
Shai White-Gilbertson et al.
Bladder (San Francisco, Calif.), 3(1) (2016-03-22)
The MB49 syngeneic, murine model of bladder cancer has been widely used for more than 35 years. In humans, bladder cancer is one third as prevalent in women as in men, with a trend toward lower prevalence in parous compared
Andreja Erman et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 22(12) (2021-07-03)
Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer is the most common form of bladder cancer. The main problem in managing bladder tumors is the high recurrence after the transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT). Our study aimed to examine the fate of intravesically applied
Pietro Strobbia et al.
Theranostics, 11(9), 4090-4102 (2021-03-24)
For the majority of cancer patients, surgery is the primary method of treatment. In these cases, accurately removing the entire tumor without harming surrounding tissue is critical; however, due to the lack of intraoperative imaging techniques, surgeons rely on visual
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務