推薦產品
一般說明
猿猴病毒(SV40)大T和小T抗原均由SV40基因组的早期区域编码。大的T抗原结合DNA,并与53,000道尔顿的细胞蛋白p53形成复合物,p53是裂解生长过程中启动病毒DNA复制所必需的。此外,大T抗原与DNA聚合酶和转录因子AP-2结合,并与视网膜母细胞瘤易感基因的P105产物形成特异性复合物。
特異性
该抗体识别SV40的大T抗原。
免疫原
纯化的SV40大T抗原
表位:SV40大T抗原
應用
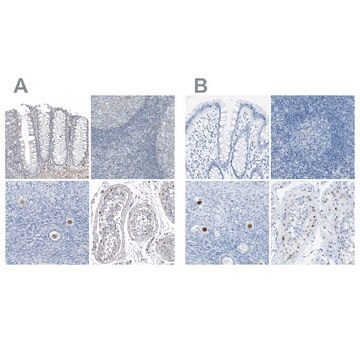
免疫细胞化学分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在ICC中检测到SV40大T抗原(Sabatier,J.,et al.(2005).58(4):429-431.; Del Valle, L., et al. (2004).J Virol.78(7):3462-3469.)。
抗SV40大T抗原抗体,克隆PAb416是抗SV40大T抗原的抗体,用于蛋白质印迹、ICC。
研究子类别
免疫球蛋白 & 免疫学
免疫球蛋白 & 免疫学
研究类别
炎症 & 免疫学
炎症 & 免疫学
品質
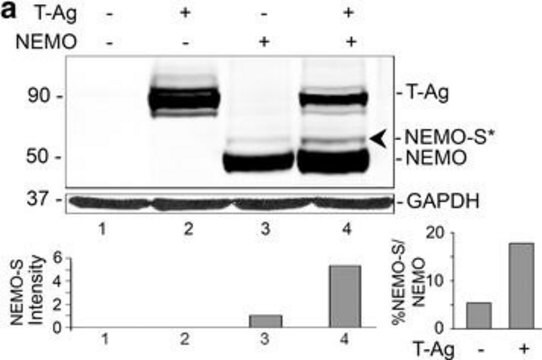
通过蛋白质印迹法在Cos-1细胞裂解物中进行评估。
蛋白质印迹分析:1 µg/mL的该抗体在10 µg Cos-1细胞裂解物中检测到SV40大T抗原。
蛋白质印迹分析:1 µg/mL的该抗体在10 µg Cos-1细胞裂解物中检测到SV40大T抗原。
標靶描述
观测分子量〜82 kDa
外觀
形式:纯化
纯化的小鼠单克隆IgG2aκ,溶于含0.1 M Tris-甘氨酸(pH 7.4)、150 mM NaCl和0.05%叠氮化钠的缓冲液中。
纯化蛋白G
儲存和穩定性
自接收之日起,在2-8°C下可稳定保存1年。
分析報告
对照
Cos-1细胞裂解物
Cos-1细胞裂解物
其他說明
浓度:关于批次特定浓度请参见检验报告。
免責聲明
除非我们的目录或产品随附的其他公司文件中另有说明,否则我们的产品预期仅用于研究用途,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或对人类或动物的任何类型的消费或应用。
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
Immunodetection of SV40 large T antigen in human central nervous system tumours.
Sabatier, J, et al.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 58, 429-431 (2005)
Primary central nervous system lymphoma expressing the human neurotropic polyomavirus, JC virus, genome.
Del Valle, Luis, et al.
Journal of virology, 78, 3462-3469 (2004)
Yasuko Orba et al.
The Journal of general virology, 92(Pt 4), 789-795 (2010-12-24)
To investigate polyomavirus infection in wild rodents, we analysed DNA samples from the spleens of 100 wild rodents from Zambia using a broad-spectrum PCR-based assay. A previously unknown polyomavirus genome was identified in a sample from a multimammate mouse (Mastomys
Ursula Neu et al.
PLoS pathogens, 9(10), e1003688-e1003688 (2013-10-17)
Viruses within a family often vary in their cellular tropism and pathogenicity. In many cases, these variations are due to viruses switching their specificity from one cell surface receptor to another. The structural requirements that underlie such receptor switching are
Furong Yuan et al.
Oncology reports, 23(2), 377-386 (2010-01-01)
Werner syndrome (WS) results from defects in the gene encoding WRN RecQ helicase. WS fibroblasts undergo premature senescence in culture. Because cellular senescence is a tumor suppressor mechanism, we examined whether WS fibroblasts exhibited reduced tumorigenicity, in comparison to control
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務