生物源
rabbit
品質等級
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
liquid
不包含
preservative
物種活性
monkey, rat, mouse, human
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
同型
IgG
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
phosphorylation (pSer317/pSer317)
基因資訊
human ... CHEK1(1111)
一般說明
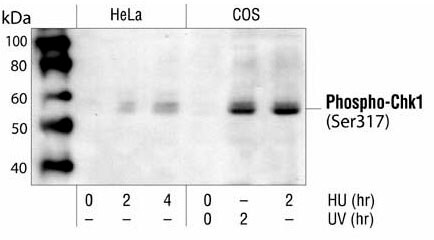
Immunoaffinity purified rabbit polyclonal antibody. Recognizes the ~56 kDa Chk1 protein when phosphorylated at Ser317.
Recognizes the ~56 kDa Chk1 protein phosphorylated at Ser317 in UV-treated COS cells.
This PhosphoDetect Anti-Chk1 (pSer³¹⁷) Rabbit pAb is validated for use in Immunoblotting, Immunocytochemistry, Paraffin Sections for the detection of Chk1 (pSer³¹⁷).
免疫原
Human
a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acids surrounding the Ser³¹⁷ phosphorylation site of human Chk1
應用
Immunoblotting (1:1000)
Immunocytochemistry (1:500, fluorescence)
Paraffin Sections (1:50)
警告
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
外觀
In 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM HEPES, 100 µg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol, pH 7.5.
重構
Do not aliquot.
分析報告
Positive Control
Lysates from COS cells treated with UV
Lysates from COS cells treated with UV
其他說明
Does not recognize unphosphorylated Chk1. Antibody should be titrated for optimal results in individual systems.
Zhao, H. and Piwnica-Worms, H. 2001. Mol. Cell. Biol.21, 4129.
Shieh, S.Y., et al. 2000. Genes Dev.14, 289.
Martinho, R.G., et al. 1998. EMBO J.17, 7239.
Zeng, Y., et al. 1998. Nature395, 507.
Shieh, S.Y., et al. 2000. Genes Dev.14, 289.
Martinho, R.G., et al. 1998. EMBO J.17, 7239.
Zeng, Y., et al. 1998. Nature395, 507.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
Helena Covelo-Molares et al.
Nucleic acids research, 49(19), 10895-10910 (2021-10-12)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and N6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) are two abundant modifications found in mRNAs and ncRNAs that can regulate multiple aspects of RNA biology. They function mainly by regulating interactions with specific RNA-binding proteins. Both modifications are linked to development, disease and
Yuki Funauchi et al.
Scientific reports, 5, 16497-16497 (2015-11-13)
Accumulation of iron in tissues increases the risk of cancer, but iron regulatory mechanisms in cancer tissues are largely unknown. Here, we report that p53 regulates iron metabolism through the transcriptional regulation of ISCU (iron-sulfur cluster assembly enzyme), which encodes
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務