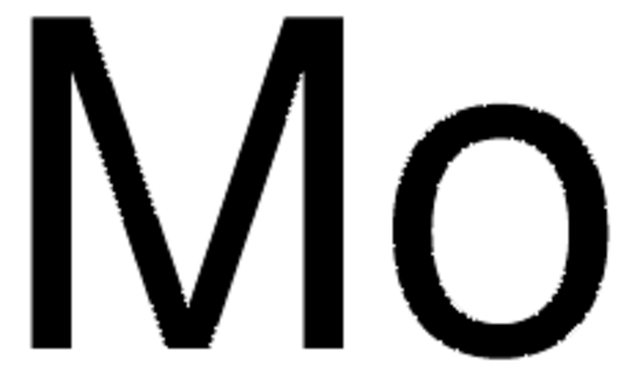推薦產品
化驗
99.90%
形狀
rod
製造商/商標名
Goodfellow 310-226-71
電阻係數
5.0 μΩ-cm, 20°C
長度 × 直徑
200 mm × 8.0 mm
bp
4612 °C (lit.)
mp
2617 °C (lit.)
密度
10.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
[Mo]
InChI
1S/Mo
InChI 密鑰
ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
For updated SDS information please visit www.goodfellow.com.
法律資訊
Product of Goodfellow
Bernd Masepohl et al.
Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 675, 49-70 (2010-06-10)
The vast majority of the purple nonsulfur photosynthetic bacteria are diazotrophs, but the details of the complex regulation of the nitrogen fixation process are well understood only for a few species. Here we review what is known of the well-studied
Ralf R Mendel et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1823(9), 1568-1579 (2012-03-01)
The transition element molybdenum (Mo) needs to be complexed by a special cofactor in order to gain catalytic activity. With the exception of bacterial Mo-nitrogenase, where Mo is a constituent of the FeMo-cofactor, Mo is bound to a pterin, thus
Angel Llamas et al.
Metallomics : integrated biometal science, 3(6), 578-590 (2011-05-31)
Molybdenum (Mo) is a very scarce element whose function is fundamental in living beings within the active site of Mo-oxidoreductases, playing key roles in the metabolism of N, S, purines, hormone biosynthesis, transformation of drugs and xenobiotics, etc. In eukaryotes
Yilin Hu et al.
Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR, 75(4), 664-677 (2011-12-01)
Nitrogenase catalyzes a key step in the global nitrogen cycle, the nucleotide-dependent reduction of atmospheric dinitrogen to bioavailable ammonia. There is a substantial amount of interest in elucidating the biosynthetic mechanisms of the FeMoco and the P-cluster of nitrogenase, because
Manuel Tejada-Jiménez et al.
Metallomics : integrated biometal science, 5(9), 1191-1203 (2013-06-27)
The viability of plants relies on molybdenum, which after binding to the organic moiety of molybdopterin forms the molybdenum cofactor (Moco) and acquires remarkable redox properties. Moco is in the active site of critical molybdoenzymes, which use to work as
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務