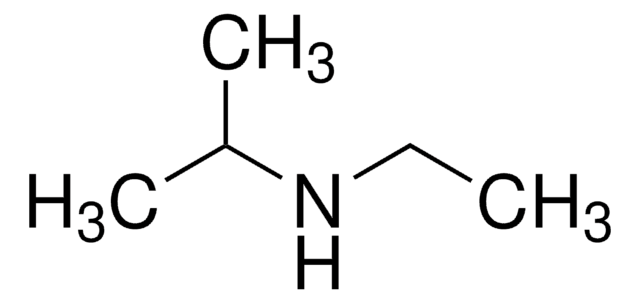
推薦產品
化驗
97%
形狀
liquid
折射率
n20/D 1.389 (lit.)
bp
63-65 °C (lit.)
密度
0.72 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
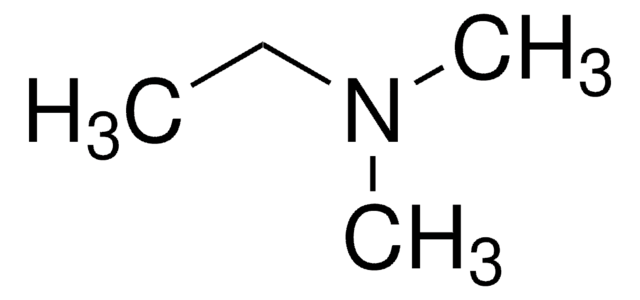
CCN(C)CC
InChI
1S/C5H13N/c1-4-6(3)5-2/h4-5H2,1-3H3
InChI 密鑰
GNVRJGIVDSQCOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
應用
- N,N-二乙基甲胺作为核磁共振130以上的线形标准 K:本研究探索了N,N-二乙基甲胺在130 K以上温度下作为核磁共振(NMR)光谱线形标准的使用,为其在高精度核磁共振分析中的应用提供了见解(Fritzsching et al., 2018)。
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B
儲存類別代碼
3 - Flammable liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
-11.2 °F - closed cup
閃點(°C)
-24 °C - closed cup
個人防護裝備
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
客戶也查看了
L Huang et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 271(23), 13401-13406 (1996-06-07)
The role played by the 6-S-cysteinyl-FMN bond of trimethylamine dehydrogenase in the reductive half-reaction of the enzyme has been studied by following the reaction of the slow substrate diethylmethylamine with a C30A mutant of the enzyme lacking the covalent flavin
Ulderico Ulissi et al.
ChemSusChem, 11(1), 229-236 (2017-09-30)
The room-temperature molten salt mixture of N,N-diethyl-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-N-methylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide ([DEME][TFSI]) and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) salt is herein reported as electrolyte for application in Li-O
P Roberts et al.
Biochemistry, 38(45), 14927-14940 (1999-11-11)
The steady-state reaction of trimethylamine dehydrogenase (TMADH) with the artificial electron acceptor ferricenium hexafluorophosphate (Fc(+)) has been studied by stopped-flow spectroscopy, with particular reference to the mechanism of inhibition by trimethylamine (TMA). Previous studies have suggested that the presence of
R J Rohlfs et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 269(49), 30869-30879 (1994-12-09)
The reductive half-reaction of trimethylamine dehydrogenase has been studied using the substrate diethylmethylamine over the pH range 6-10. It is found that the reaction occurs with three distinct and, under most conditions, fully resolved kinetic phases. The hyperbolic substrate concentration
Lihua Huang et al.
Analytical chemistry, 81(2), 567-577 (2008-12-17)
PEGylation of peptides and proteins presents significant challenges for structural characterization due to the heterogeneity of the poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), the number of PEG moieties attached, and the site(s) of PEGylation. In this work, a novel and powerful methodology using
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務