919403
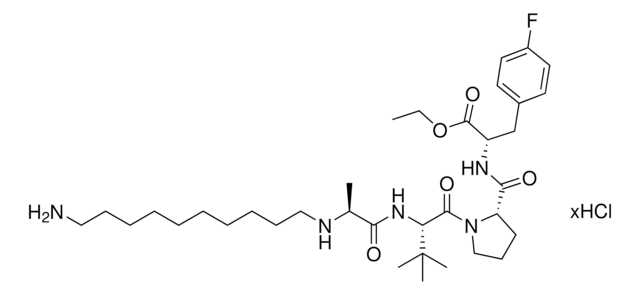
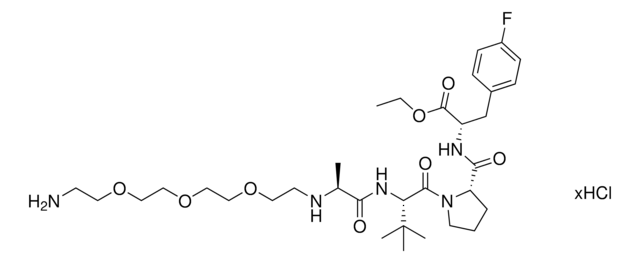
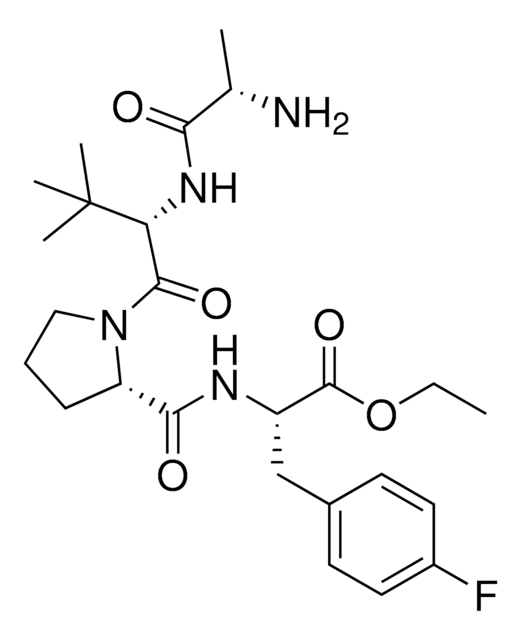
CCW16-C4-BocNH
95%
同義詞:
tert-Butyl (4-(4-(4-(N-benzyl-2-chloroacetamido)phenoxy)phenoxy)butyl)carbamate, Crosslinker-E3 Ligase ligand conjugate, Protein degrader building block for PROTAC® research, RNF4-targeting building block, Template for synthesis of targeted protein degrader
登入查看組織和合約定價
全部照片(2)
About This Item
推薦產品
ligand
CCW16
品質等級
化驗
95%
形狀
viscous liquid
反應適用性
reactivity: carboxyl reactive
reagent type: ligand-linker conjugate
官能基
amine
儲存溫度
2-8°C
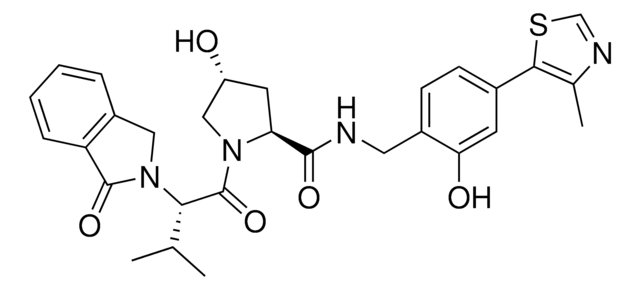
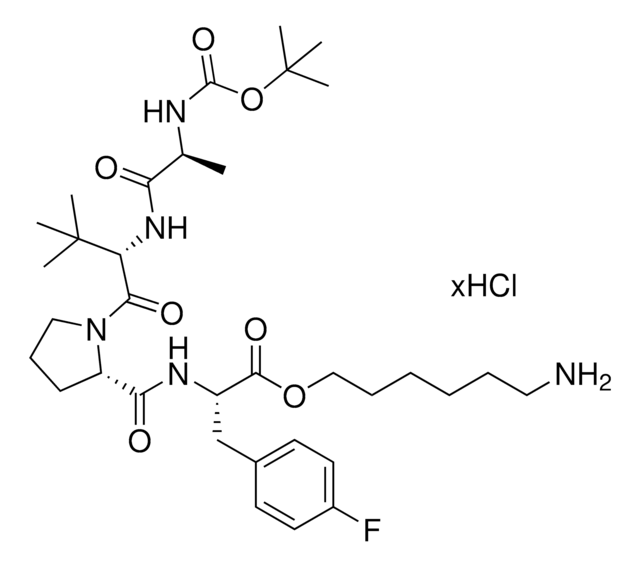
SMILES 字串
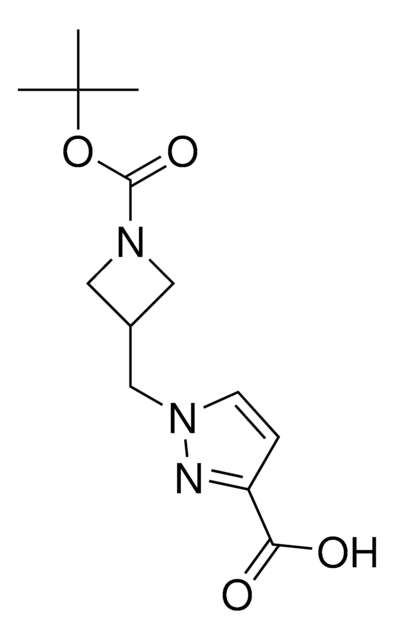
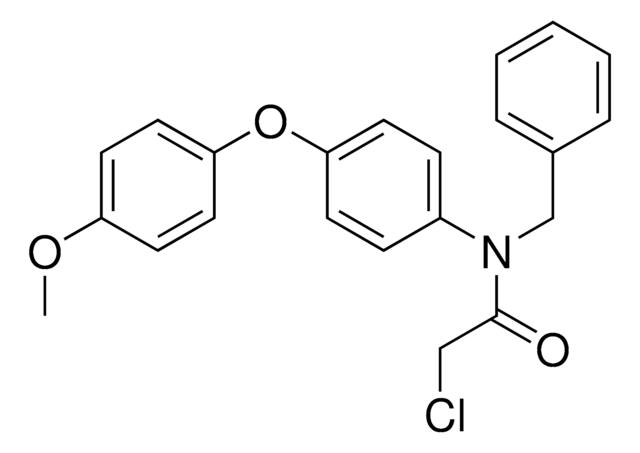
O=C(CCl)N(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)OC3=CC=C(OCCCCNC(OC(C)(C)C)=O)C=C3
InChI
1S/C30H35ClN2O5/c1-30(2,3)38-29(35)32-19-7-8-20-36-25-15-17-27(18-16-25)37-26-13-11-24(12-14-26)33(28(34)21-31)22-23-9-5-4-6-10-23/h4-6,9-18H,7-8,19-22H2,1-3H3,(H,32,35)
InChI 密鑰
JABXXARCXCVEGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
應用
Protein degrader builiding block CCW16-C4-BocNH enables the synthesis of molecules for targeted protein degradation and PROTAC (proteolysis-targeting chimeras) technology. This conjugate contains a RING finger protein 4 (RNF4)-recruiting ligand, an alkyl-chain crosslinker, and a pendant amine for reactivity with a carboxylic acid on the target ligand. Because even slight alterations in ligands and crosslinkers can affect ternary complex formation between the target, E3 ligase, and PROTAC, many analogs are prepared to screen for optimal target degradation. When used with other protein degrader building blocks with a pendant amine, parallel synthesis can be used to more quickly generate PROTAC libraries that feature variation in crosslinker length, composition, and E3 ligase ligand.
其他說明
法律資訊
PROTAC is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license
相關產品
產品號碼
描述
訂價
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Momar Toure et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 55(6), 1966-1973 (2016-01-13)
The current inhibitor-based approach to therapeutics has inherent limitations owing to its occupancy-based model: 1) there is a need to maintain high systemic exposure to ensure sufficient in vivo inhibition, 2) high in vivo concentrations bring potential for off-target side effects, and 3) there is
Daniel P Bondeson et al.
Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 57, 107-123 (2016-10-13)
Protein homeostasis networks are highly regulated systems responsible for maintaining the health and productivity of cells. Whereas therapeutics have been developed to disrupt protein homeostasis, more recently identified techniques have been used to repurpose homeostatic networks to effect degradation of
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務