推薦產品
應用
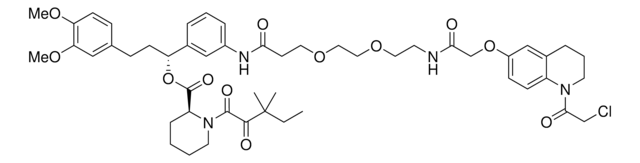
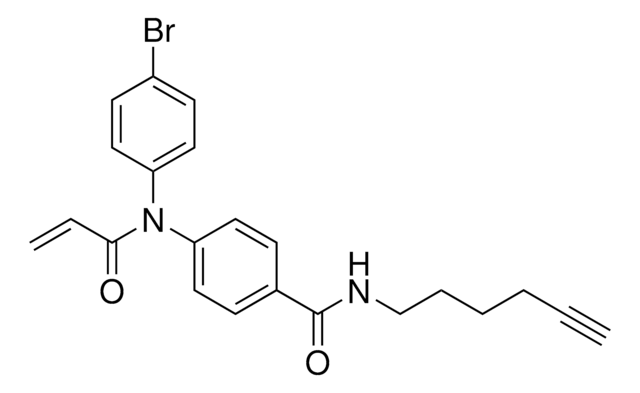
N-(4-Bromophenyl)-N-phenylacrylamide is a cysteine-reactive small-molecule fragment for chemoproteomic and ligandability studies for both traditionally druggable proteins as well as ″undruggable,″ or difficult-to-target, proteins. This fragment electrophile, or ″scout″ fragment, can be used alone in fragment-based covalent ligand discovery or incorporated into bifunctional tools such as electrophilic PROTAC® molecules for targeted protein degradation as demonstrated by the Cravatt Lab for E3 ligase discovery.
其他說明
法律資訊
PROTAC is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license
相關產品
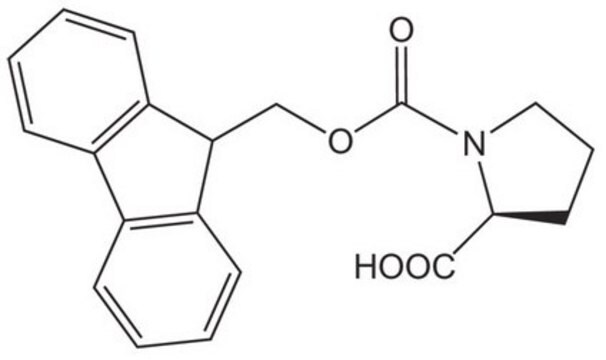
產品號碼
描述
訂價
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
Keriann M Backus et al.
Nature, 534(7608), 570-574 (2016-06-17)
Small molecules are powerful tools for investigating protein function and can serve as leads for new therapeutics. Most human proteins, however, lack small-molecule ligands, and entire protein classes are considered 'undruggable'. Fragment-based ligand discovery can identify small-molecule probes for proteins
Xiaoyu Zhang et al.
Nature chemical biology, 15(7), 737-746 (2019-06-19)
Ligand-dependent protein degradation has emerged as a compelling strategy to pharmacologically control the protein content of cells. So far, however, only a limited number of E3 ligases have been found to support this process. Here, we use a chemical proteomic
文章
Ligandability describes the propensity of a protein target to bind a small molecule with high affinity. It is a precursor to evaluating druggability, which requires more advanced translational pharmacological effects and drug-like properties in vivo.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務