推薦產品
形狀
chunks
饋電比
lactide:caprolactone 90:10
顏色
white to off-white
黏度
1.7 dL/g
儲存溫度
−20°C
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
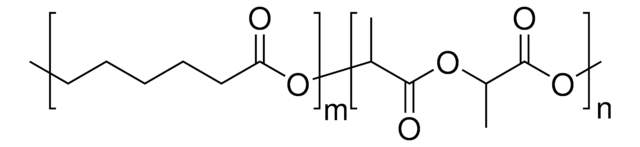
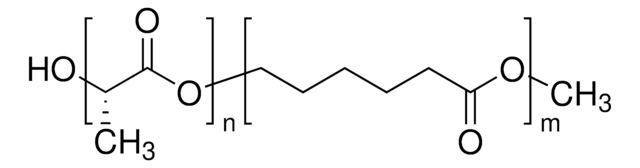
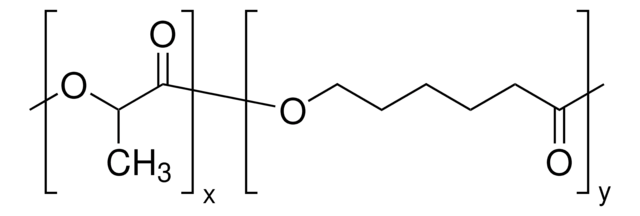
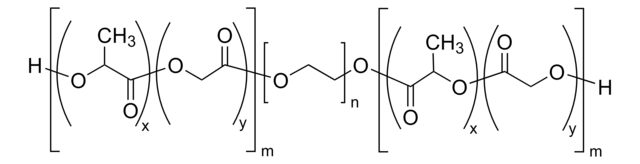
Poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone) (PCL-PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer which can be synthesized by bulk ring-opening copolymerization of L-lactide and ε-caprolactone. Its properties include flexibility, biocompatibility and controlled degradation process.
應用
PCL-PLLA can be used for a variety of applications such as tissue engineering, bone fixation devices and surgical sutures.
Poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone) (PLLA-PCL) is a biodegradable copolymer. poly(L-lactide) exhibits a high modulus and has been often copolymerized with PCL to improve the mechanical properties of PCL, and increase degradation rate of the resulting polymer. PLLA-PCL has been used in tissue engineering, 3D bioprinting and drug delivery research applications.
儲存類別代碼
13 - Non Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Comparison of plasma and chemical modifications of poly-L-lactide-co-caprolactone scaffolds for heparin conjugation
Hsieh Y, et al.
Bio-medical materials and engineering, 12(6), 065004-065004 (2017)
Preclinical animal study and human clinical trial data of co-electrospun poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone) and fibrinogen mesh for anterior pelvic floor reconstruction
Wu X, et al.
International journal of nanomedicine, 11(6), 389-389 (2016)
Fabrication and characterization of vitamin B5 loaded poly (l-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fiber aligned electrospun nanofibers for schwann cell proliferation
Bhutto MA, et al.
Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 144(6), 108-117 (2016)
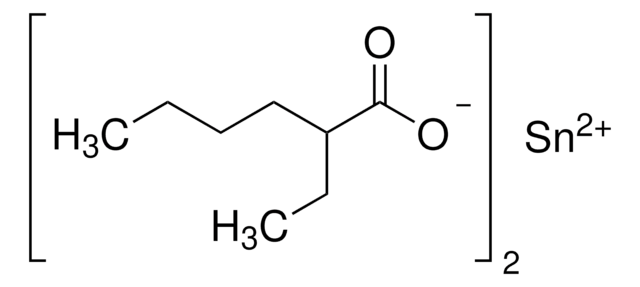
Preparation of a poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone) copolymer using a novel tin (II) alkoxide initiator and its fiber processing for potential use as an absorbable monofilament surgical suture
Ruengdechawiwat S, et al.
International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials, 65(6), 277-284 (2016)
Application of a bilayer tubular scaffold based on electrospun poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/collagen fibers and yarns for tracheal tissue engineering
Wu T, et al.
Journal of materials chemistry. B, 5(1), 139-150 (2017)
文章
Professor Nicola Tirelli (Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Italy) highlights the microfluidic-assisted method for fabricating well-defined and reproducible nanoparticles for drug delivery research.
Professor Nicola Tirelli (Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Italy) highlights the microfluidic-assisted method for fabricating well-defined and reproducible nanoparticles for drug delivery research.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務