SML2475
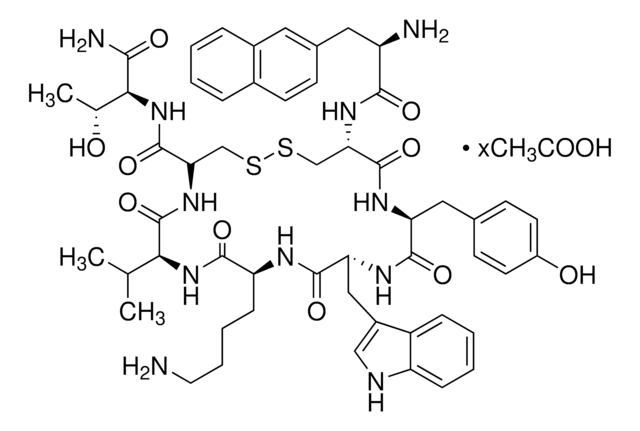
Larazotide acetate salt
≥95% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
AT-1001, AT1001, GGVLVQPG acetate, Glycylglycyl-L-valyl-L-leucyl-L-valyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-glycine acetate
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white to beige
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
N1([C@@H](CCC1)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CNC(=O)CN)C(C)C)CC(C)C)C(C)C)CCC(=O)N.OC(=O)C
InChI
1S/C32H55N9O10.C2H4O2/c1-16(2)12-20(38-30(49)26(17(3)4)39-24(44)14-35-23(43)13-33)28(47)40-27(18(5)6)31(50)37-19(9-10-22(34)42)32(51)41-11-7-8-21(41)29(48)36-15-25(45)46;1-2(3)4/h16-21,26-27H,7-15,33H2,1-6H3,(H2,34,42)(H,35,43)(H,36,48)(H,37,50)(H,38,49)(
InChI key
NYGCNONRVCGHAT-UFIKZEAMSA-N
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service