S4521
Saponin from Quillaja sp.
Sapogenin content 20-35 %
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
non-ionic
composition
Sapogenin content, 20-35%
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
protein quantification: suitable
sulfated ash
≤10%
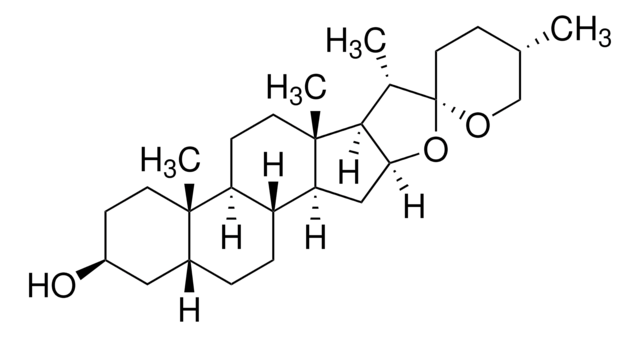
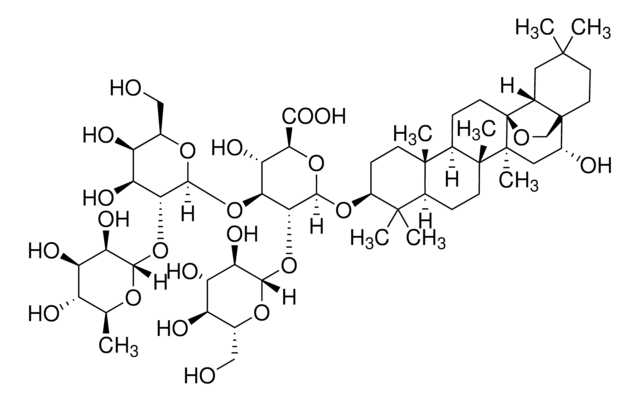
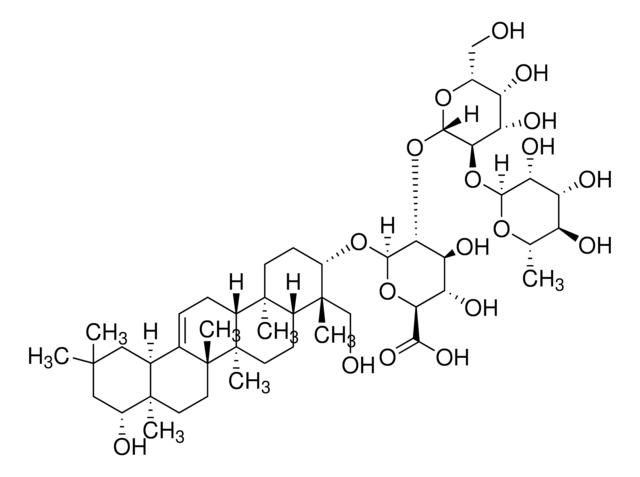
SMILES string
O1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1CO)O)O)O)O[C@H]2[C@@H](O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]8O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]8O)O)O)CO)C(=O)O)O[C@@H]3[C@@](C4[C@@](C5[C@]([C@@]6(C[C@H]([C@]7([C@H]([C@@H](C(CC7C6=CC5)(C)C)OC(=O)\C(=C/C)\C)OC(=O)C)CO)O)C)(CC4)C)(CC3)C
InChI
1S/C55H86O24/c1-10-23(2)46(71)79-43-44(72-24(3)60)55(22-59)26(17-50(43,4)5)25-11-12-30-51(6)15-14-32(52(7,21-58)29(51)13-16-53(30,8)54(25,9)18-31(55)61)75-49-41(77-48-38(67)36(65)34(63)28(20-57)74-48)39(68)40(42(78-49)45(69)70)76-47-37(66)35(64)33(62)27(1
InChI key
AXNVHPCVMSNXNP-ZELRDNAQSA-N
General description
Application
- to stain fertilized oocytes
- in the analysis of intracellular cytokine production
- to permeabilize dendritic cells
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service