L2254
Lipoprotein Lipase from bovine milk
ammonium sulfate suspension, ≥2,000 units/mg protein (BCA)
Synonym(s):
LPL, Phospholipase A1, Diacylglycerol acylhydrolase, Diacylglycerol lipase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine milk
Quality Level
form
ammonium sulfate suspension
specific activity
≥2,000 units/mg protein (BCA)
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) from bovine milk is a glycoprotein. It exists as a homodimer and comprises two N-linked oligosaccharides. It is heat-labile.Lipoprotein lipase is an enzyme found on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, where it is anchored to capillary walls. It is mainly present in adipose tissue, heart, and muscle tissue. It is synthesized by extrahepatic tissues, particularly adipocytes, and the gene encoding the protein is situated on chromosome 8p22.
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) from bovine milk is a glycoprotein. It exists as a homodimer and comprises two N-linked oligosaccharides. It is heat-labile.Lipoprotein lipase is an enzyme found on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, where it is anchored to capillary walls. It is mainly present in adipose tissue, heart, and muscle tissue. It is synthesized by extrahepatic tissues, particularly adipocytes, and the gene encoding the protein is situated on chromosome 8p22.
Application
Lipoprotein Lipase from bovine milk has been used:
- as a supplement to test its effect on DiI (1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′-tetramethyl-indocarbocyanine perchlorate)- very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) uptake in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
- to treat human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) for the lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRL).
- to test its effect on gene expression in normal human astrocytes.
- in primary hepatocyte isolation and lipoprotein binding to identify Sulf2 inhibition in T2DM mice for improving diabetic dyslipidemia.
- in transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1) immunoassay to test if the TGF-β signaling system regulates the up-regulation and activation of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) induced by lipolysis products.
- in human TGRL isolation.
- in in vitro lipolysis assay with HSPG-bound LPL, to investigate the effect of human apoE2 (Lys146→Gln) on lipoprotein metabolism.
- in hydrolysis of triglycerides.
- in developing in vitro model of gastrointestinal digestion to investigate the effects of chlorophyll on lipid digestion.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) from bovine milk contributes to maximal lipolytic activity. It associates with casein micelle. LPL regulates triglyceride utilization and displays positional specificity. Lipases, in general, catalyzes the lipolysis of triglycerides especially at the fatty acid in sn-1 and sn-3 positions of the triglyceride.LPL is known to significantly impact the advancement of atherosclerosis. Studies have indicated that advanced atherosclerosis patients display increased LPL mass and activity in their post-heparin plasma.
Unit Definition
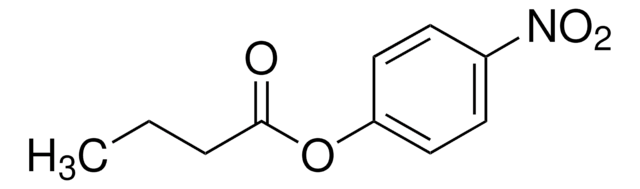
One unit will release 1.0 nmole of p-nitrophenol per min at pH 7.2 at 37 °C using p-nitrophenyl butyrate as substrate.
Physical form
Suspension in 3.8 M ammonium sulfate, 0.02 M Tris HCl, pH 8.0
Preparation Note
Affinity purified
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Richard E Morton et al.
Journal of lipid research, 63(2), 100166-100166 (2022-01-13)
Apolipoprotein F (ApoF) modulates lipoprotein metabolism by selectively inhibiting cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity on LDL. This ApoF activity requires that it is bound to LDL. How hyperlipidemia alters total plasma ApoF and its binding to LDL are poorly understood.
Leslie E Lupien et al.
Journal of lipid research, 61(2), 205-218 (2019-12-07)
We previously described the expression of CD36 and LPL by breast cancer (BC) cells and tissues and the growth-promoting effect of VLDL observed only in the presence of LPL. We now report a model in which LPL is bound to
Dean Oldham et al.
Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 9, 926631-926631 (2022-08-02)
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) plays a crucial role in preventing dyslipidemia by hydrolyzing triglycerides (TGs) in packaged lipoproteins. Since hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), the leading cause of death worldwide, methods that accurately quantify the
Shin-Ichi Yokota et al.
Infection and immunity, 78(1), 468-476 (2009-10-28)
Helicobacter pylori is recognized as an etiological agent of gastroduodenal diseases. H. pylori produces various toxic substances, including lipopolysaccharide (LPS). However, H. pylori LPS exhibits extremely weakly endotoxic activity compared to the typical LPS, such as that produced by Escherichia
Silvia Hilt et al.
Frontiers in chemistry, 10, 896386-896386 (2022-06-21)
Several neurodegenerative diseases are driven by misfolded proteins that assemble into soluble aggregates. These "toxic oligomers" have been associated with a plethora of cellular dysfunction and dysregulation, however the structural features underlying their toxicity are poorly understood. A major impediment
Articles
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Heart Disease
Lipid Induced Insulin Resistance
Instructions for working with enzymes supplied as ammonium sulfate suspensions
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service