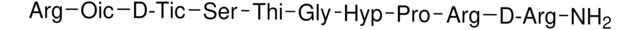H7016
Hirudin
from leeches, ≥1,500 ATU/mg protein, lyophilized powder
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Hirudin from leeches, lyophilized powder, ≥1,500 ATU/mg protein (ATU = antithrombin units)
biological source
animal (Hirudo verbana)
Quality Level
100
200
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥1,500 ATU/mg protein (ATU = antithrombin units)
mol wt
7 kDa
solubility
pyridine: soluble
water: soluble
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Hirudin is a 7 kDa acidic protein containing 65 amino acid residues that has an isoelectric point of 3.5-4.0. It is not glycosylated and lacks tryptophan, arginine and methionine residues. It is chemically stable between pH 2-12 and at temperatures up to 80°C.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The anticoagulant, hirudin, is the most potent natural inhibitor of both soluble and clot-bound thrombin. It binds thrombin with high affinity, covering more than 20% of its surface area and occluding both the active site and exosite I (fibrinogen and PAR recognition site). Hirudin blocks thrombus growth and platelet activation. It is not metabolized in the bloodstream of humans and is eliminated unchanged via kidney filtration.
The anticoagulant, hirudin, is the most potent natural inhibitor of both soluble and clot-bound thrombin. It forms a high-affinity 1:1 complex with thrombin, occluding both the proteolytic site and exosite I (fibrinogen and PAR recognition site). Hirudin blocks thrombus growth and platelet activation, and has been suggested as the clinically preferred anticoagulant (over heparin and citrate) for its specific mode of action and absence of side effects. It is not metabolized in the bloodstream of humans and is eliminated unchanged via kidney filtration.
Unit Definition
One unit (ATU) will neutralize one NIH unit of thrombin at 37 °C, based on direct comparison to an NIH thrombin reference standard.
Analysis Note
Protein determined by Lowry.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sarah E Sartain et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 196(2), 832-845 (2015-12-18)
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a thrombotic microangiopathy with severe renal injury secondary to an overactive alternative complement pathway (AP). aHUS episodes are often initiated or recur during inflammation. We investigated gene expression of the surface complement regulatory proteins
Mengzhou Xue et al.
Brain : a journal of neurology, 132(Pt 1), 26-36 (2008-09-06)
Proteases such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and thrombin are implicated in intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) but their interactions amongst one another and interdependency remain to be defined. The latter is important since proteases acting through different mechanisms to inflict neurotoxicity would
Yaoming Wang et al.
Stroke, 40(5), 1864-1869 (2008-12-06)
Activated protein C (APC), a protease with anticoagulant and cytoprotective activities, protects neurons and endothelium from ischemic injury. Drotrecogin-alfa activated, a hyperanticoagulant form of human recombinant APC, is currently being studied in patients with ischemic stroke. How changes in APC
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service


![[Tyr(SO3H)63]-Hirudin Fragment 54-65 ≥95% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/401/056/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097/640/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097.png)