378348
Silicone oil
viscosity 20 cSt (25 °C)
Synonym(s):
PDMS, Polydimethylsiloxane
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
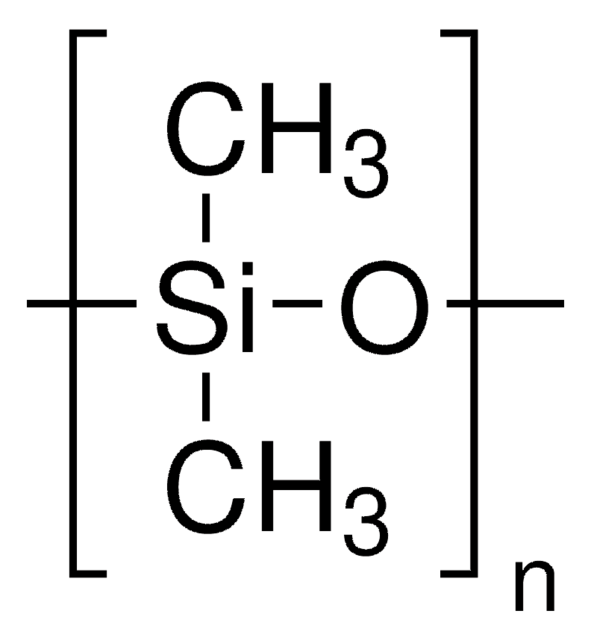
Linear Formula:
[-Si(CH3)2O-]n
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
<5 mmHg ( 25 °C)
5 mmHg ( 20 °C)
form
viscous liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.403 (lit.)
viscosity
20 cSt(25 °C)
bp
>140 °C/0.002 mmHg (lit.)
density
0.95 g/mL at 25 °C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Silicone oil is a liquid based siloxane that is part of the methyl silicone fluid system. It has a viscosity of 20 cSt with a refractive index of ~ 1.4 and a dielectric strength of ~ 14 kV/mm. It′s surface tension tends to increase with an increase in the viscosity.
Application
Silicone oil can be used for a variety of usages such as lubricants, antiflatulent agents, dielectric coolants, and cosmetic additives.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
214.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
101.1 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Antifoaming agents
Owen MJ
Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 104(2), 527-535 (2001)
Silicones
Moretto H, et al.
Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (2000)
Mechanism of Stabilization of Silicone Oil- Water Emulsions Using Hybrid Siloxane Polymers
Mehta SC and Somasundaran P
Langmuir, 24(9), 4558-4563 (2008)
Tindaro Ioppolo et al.
Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE, (71)(71), e50199-e50199 (2013-02-15)
Optical modes of dielectric micro-cavities have received significant attention in recent years for their potential in a broad range of applications. The optical modes are frequently referred to as "whispering gallery modes" (WGM) or "morphology dependent resonances" (MDR) and exhibit
M Brun et al.
Conference proceedings : ... Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual Conference, 2012, 6281-6284 (2013-02-01)
This paper demonstrates the potential use of a new microfluidic device embedding thick electrodes for cell lysis and cell separation applications. The system consists of a microfluidic channel featuring conductive walls made of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrix mixed with carbon
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service