R5506
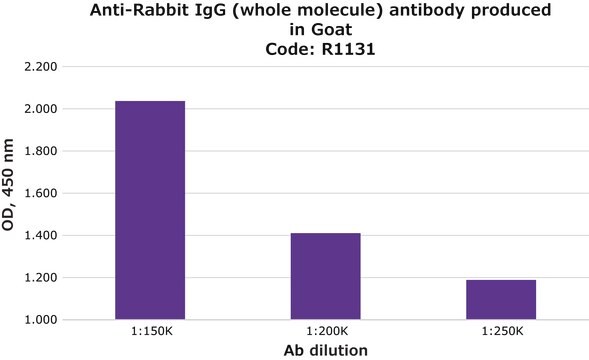
Anti-Rabbit IgG (whole molecule) antibody produced in goat
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Rabbit IgG Antibody
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
goat
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
IgG fraction of antiserum
antibody product type
secondary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
indirect ELISA: 1:30,000
quantitative precipitin assay: 3.0-4.5 mg/mL
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Immunoglobulins (Igs) belong to the immunoglobulin super-family and have two heavy (H) and two light (L) chains, held together by disulfide linkages. The heavy chain has one variable N-terminal region and three to four constant (CH1-CH4) C-terminal regions. The L chain comprises of one variable N-terminal region and a constant C-terminal region. IgG is an abundant protein in human serum. The four classes of IgG include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. The IgG heavy chain region is mapped to human chromosome 14.
Rabbit immunoglobulins (IgGs) are often used as primary antibodies in several protein assays. Thus, anti-rabbit IgGs can be used as secondary antibodies to study and characterize target proteins bound to rabbit IgGs. Anti-Rabbit IgG (whole molecule) antibody is specific for IgGs in rabbits.
Specificity
Anti-Rabbit IgG (whole molecule) antibody is specific for IgGs in rabbits.
Immunogen
Rabbit IgG
Application
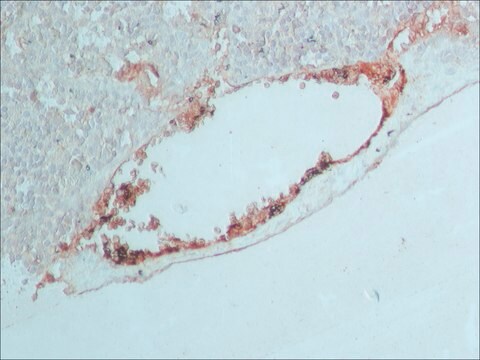
Anti-Rabbit IgG (whole molecule) antibody is suitable for use in quantitative precipitin assay, immunoelectrophoresis, immunohistochemistry , and laser scattering microscopy .
Anti-Rabbit IgG (whole molecule) antibody produced in goat has been used as secondary antibody in vivo xenograft assay in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues and in western blotting detection in endometrial sample from cattle.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Digestion of IgG by papain results in the generation of fragment antigen binding (Fab). Pepsin digestion of IgG produces fragment crystallizable (Fc). The Fc region of IgG antibody has enormous therapeutic potential and is exploited for the development of therapeutic antibodies. IgG1 class is the most abundant and its deficiency results in hypogammaglobulinemia. IgG2 deficiency increases susceptibility to bacterial infections. IgG3 mediates effector functions, and IgG4 is associated with asymptomatic infection.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide as preservative
Storage and Stability
For continuous use, store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, the solution may be frozen in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frost-free" freezers is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
The newly established bovine endometrial gland cell line (BEGC) forms gland acini in vitro and is only IFNtau-responsive after E2 and P4-pre-incubation.
Haeger JD, et al.
Placenta, 15(2), 1633-1639 (2018)
Steven Johnson et al.
Nature microbiology, 6(6), 712-721 (2021-05-02)
The bacterial flagellum is a macromolecular protein complex that enables motility in many species. Bacterial flagella self-assemble a strong, multicomponent drive shaft that couples rotation in the inner membrane to the micrometre-long flagellar filament that powers bacterial swimming in viscous
Junhua Yuan et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(4), 1182-1185 (2008-01-19)
Flagellated bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, are propelled by helical flagellar filaments, each driven at its base by a reversible rotary motor, powered by a transmembrane proton flux. Torque is generated by the interaction of stator proteins, MotA and MotB
MicroRNA-30a suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting Myb-related protein B.
Geng GJ, et al.
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 15(2), 1633-1639 (2018)
D Bässler et al.
The Journal of experimental biology, 199(Pt 11), 2369-2382 (1996-11-01)
1. The common inhibitory motoneurone 1 (CI1) in the mesothoracic ganglion of the locust was photoinactivated using a helium-cadmium laser or a mercury lamp as light source. Treated animals showed no signs of abnormal locomotory behaviour over periods of up
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service