H0402
Heparin−Agarose
(1:1 suspension in a 20% ethanol solution)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
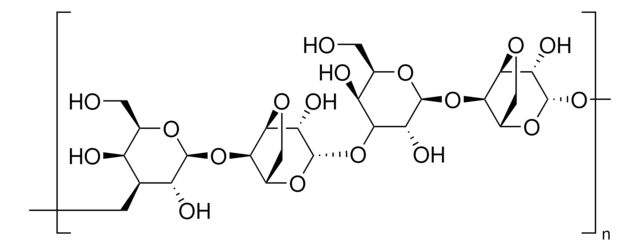
biological source
heparin from Porcine intestinal mucosa
form
(1:1 suspension in a 20% ethanol solution)
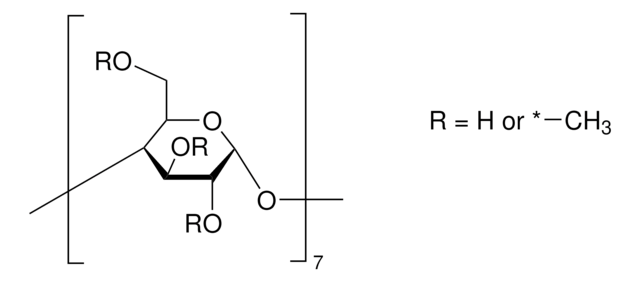
matrix
4% beaded agarose
matrix activation
epichlorohydrin
matrix attachment
terminal aldehyde by reductive amination to amine linker
matrix spacer
7 atoms
capacity
≥0.5 mg/mL binding capacity (thrombin)
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Heparin agarose is developed from porcine intestinal mucosa and is used in affinity chromatography. Heparin agarose has been used in studies to provide information on human monocytic ehrlichiosis, tumor necrosis and the effects of coagulation from Vipera snake venom.
Physical form
1:1 suspension in a 20% ethanol solution
Preparation Note
Prepared by end-point attachment for high-efficiency fractionation of antithrombin III and other specific binding proteins
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 3
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
104.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
40 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Kenji Kashiwagi et al.
Biomaterials, 30(6), 1166-1175 (2008-11-22)
Efficient immobilization of biomacromolecules on material surfaces is a key to development in areas of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. However, strong and irreversible immobilization of cytokines on surfaces often diminishes their biological functionality. A destructive hydrophobic interaction between the
W H Yu et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 275(6), 4183-4191 (2000-02-08)
Many matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are tightly bound to tissues; matrilysin (MMP-7), although the smallest of the MMPs, is one of the most tightly bound. The most likely docking molecules for MMP-7 are heparan sulfate proteoglycans on or around epithelial cells
Glycosaminoglycan binding assays.
A J Hoogewerf et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 138, 173-177 (2000-06-07)
B A Kluszynski et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 272(21), 13541-13547 (1997-05-23)
We have studied the ability of histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) to neutralize the anticoagulant activity of heparin in plasma and in a purified component clotting assay. Addition of HRG to plasma or to the purified component assay did not neutralize the
Miriam Corredor et al.
Biophysical journal, 110(6), 1291-1303 (2016-03-31)
Semaphorin3A (Sema3A) is a vertebrate-secreted protein that was initially characterized as a repulsive-guidance cue. Semaphorins have crucial roles in several diseases; therefore, the development of Sema3A inhibitors is of therapeutic interest. Sema3A interacts with glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), presumably through its C-terminal
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service