E7033
pFLAG-CMV-2 Expression Vector
shuttle vector for intracellular transient expression of N-terminal Met-FLAG
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
FLAG® tagged
grade
for molecular biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
quality
shuttle vector for intracellular transient expression of N-terminal Met-FLAG
Peptide tag location
N-terminal
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
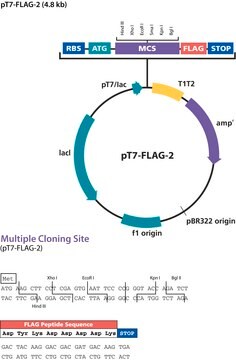
The pFLAG-CMV™-2 Expression Vector is a 4.7 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector1 for intracellular expression of N-terminal Met-FLAG® fusion proteins in mammalian cells.
pFLAG-CMV-2 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The pFLAG-CMV-2-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.1 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector1 for intracellular expression of N-terminal Met-FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells.
Vector Maps and Sequences
pFLAG-CMV-2 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The pFLAG-CMV-2-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.1 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector1 for intracellular expression of N-terminal Met-FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells.
Vector Maps and Sequences
Components
- pFLAG-CMV™-2 Expression Vector 20 μg (E7398) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 in 1 mM EDTA.
- pFLAG-CMV™-2-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (P5100) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus drives transcription of FLAG®-fusion constructs.
Legal Information
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
pFLAG-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Jing Ouyang et al.
Blood, 117(16), 4315-4322 (2011-02-09)
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs) are potentially fatal, EBV-driven B-cell malignancies that develop in immunocompromised solid organ or hematopoietic stem cell recipients. In PTLD, the expression of EBV proteins, including latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) and LMP2A, viral immune evasion strategies
Li Yang et al.
Cancer research, 67(12), 5587-5593 (2007-06-19)
Evidence indicates that the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and high prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels contribute to the pathogenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In addition to overproduction by COX-2, PGE2 concentrations also depend upon the levels of the PGE2 catabolic
Michiko Tanaka et al.
Virology journal, 5, 125-125 (2008-10-23)
The herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) UL7 gene is highly conserved among herpesviridae. Since the construction of recombinant HSV-1 with a mutation in the UL7 gene has not been reported, the involvement of HSV-1 UL7 in viral replication has been
Chun-Hung Lin et al.
The FEBS journal, 274(11), 2946-2956 (2007-05-10)
The mammalian nitrilase (Nit) protein is a member of the nitrilase superfamily whose function remains to be characterized. We now show that the nitrilase family member 2 gene (NIT2) is ubiquitously expressed in multiple tissues and encodes protein mainly distributed
Kohsuke Tsuchiya et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 185(2), 1186-1195 (2010-06-23)
Listeria monocytogenes invades the cytoplasm of macrophages and induces the activation of caspase-1 and the subsequent maturation of IL-1beta and IL-18. Although apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-activating and recruitment domain (ASC), an adaptor protein of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (Nod)-like
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service