B107
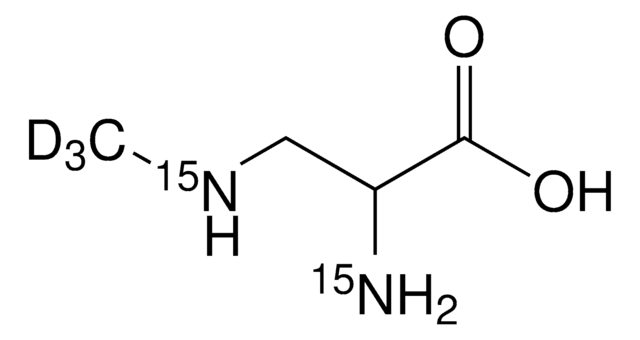
L-BMAA hydrochloride
≥97% (NMR), powder
Synonym(s):
S(+)-2-Amino-3-(methylamino)propionic acid hydrochloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C4H10N2O2 · HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
154.60
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Assay
≥97% (NMR)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]/D +21 to +31°, c = 0.5 M in 0.1 M HCl(lit.)
storage condition
desiccated
color
white to beige
solubility
H2O: soluble (solutions may be stored for several days at 4 °C)
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CNC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H10N2O2.ClH/c1-6-2-3(5)4(7)8;/h3,6H,2,5H2,1H3,(H,7,8);1H/t3-;/m0./s1
InChI key
VDXYGASOGLSIDM-DFWYDOINSA-N
General description
L-BMAA hydrochloride/β-N-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA) is a cyanobacterial neurotoxin.
Application
L-BMAA hydrochloride has been used as a standard to compare all the samples in the analysis of β-N-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA) isomers in desert crust material. It has also been used as an additive with f/2+Si medium to treat the cells of Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Thalassiosira weissflogii to study its effect on them.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-BMAA hydrochloride helps to block the addition of heparan sulfate to glypican-1. It possesses unusual glutamate receptor binding properties. It may cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/Lou Gehrig′s disease.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Neurotoxic amino acids and their isomers in desert environments
Metcalf JS, et al.
Journal of arid environments, 140-144 (2015)
David A Davis et al.
Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology, 79(4), 393-406 (2020-02-23)
The early neuropathological features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease (ALS/MND) are protein aggregates in motor neurons and microglial activation. Similar pathology characterizes Guamanian ALS/Parkinsonism dementia complex, which may be triggered by the cyanotoxin β-N-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA). We report here the
Olga A Koksharova et al.
Toxins, 12(6) (2020-06-10)
All cyanobacteria produce a neurotoxic non-protein amino acid β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA). However, the biological function of BMAA in the regulation of cyanobacteria metabolism still remains undetermined. It is known that BMAA suppresses the formation of heterocysts in diazotrophic cyanobacteria under nitrogen
2-Amino-β-methylamino-propionc acid, a new amino acid from seeds of Cycas circinali.
Vega, et al.
Psychochemistry, 6, 759-762 (1967)
Johan Eriksson et al.
Amino acids, 36(1), 43-48 (2008-01-12)
Two different assays have been developed and used in order to investigate the optimal conditions for derivatization and detection of acid beta-N-methyl-amino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a cyanobacterial sample. BMAA was extracted from cyanobacterial cultures both from the cytosolic ("free") fraction and
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service