ACOA-RO
Roche
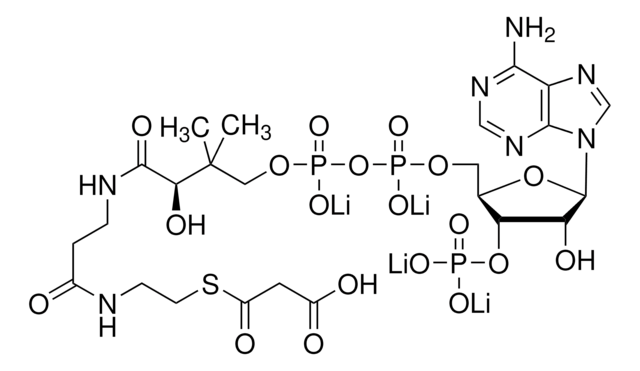
Acetyl-Coenzyme A
85% (Enzymatic and Absorbance), 2% (lithium)
Synonym(s):
Acetyl-Coenzyme A, acetyl-coa
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
Recommended Products
description
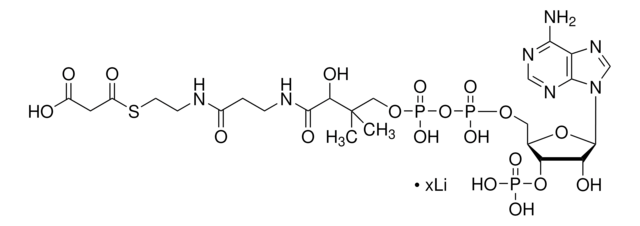
Chemical Formula: C23H35N7O17P3SLi3
Quality Level
Assay
85% (Enzymatic and Absorbance)
form
solid
mol wt
Mr 809.6 (acetyl-CoA)
Mr 827.4 (acetyl-CoA-Li3)
packaging
pkg of 010 mg (10101893001)
pkg of 200 mg (11585371001)
pkg of 050 mg (10101907001)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
concentration
2% (lithium)
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Acetyl-Coenzyme A, trilithium salt
Application
Acetyl-Coenzyme A is used to assay CAT enzyme activity in cell extracts using radioisotopes. CAT enzyme activity in cell extracts catalyzes the transfer of acetyl groups from acetylcoenzyme A to chloramphenicol. A number of assays have been developed to measure CAT activity in cell extracts. Acetyl-Coenzyme A has also been used to determine citrate synthase activity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Acetyl-Coenzyme A (Ac-CoA) is the end product of glycolysis and takes part in the Ac-CoA pathway, which is a metabolic pathway for carbon compounds. Ac-CoA is important in cholesterol synthesis. It also takes part in fatty acid biosynthesis and catabolism of polyamines like spermine and spermidine. A low level of Ac-CoA leads to a loss in glial cell and neuronal function. Ketone bodies and triglycerides give rise to Ac-CoA on hydrolysis and this indirectly leads to increased histone acetylation.
Preparation Note
Working solution: Optimal solvent: water or aqueous solution with a weak acidic pH (4 to 5).
Storage conditions (working solution): -15 to -25 °C
50 mg/ml in phosphate buffer, pH 7, is stable for 3 weeks at -15 to -25 °C. Unfrozen solutions should be immediately used.
Storage conditions (working solution): -15 to -25 °C
50 mg/ml in phosphate buffer, pH 7, is stable for 3 weeks at -15 to -25 °C. Unfrozen solutions should be immediately used.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
L Lu et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 271(31), 18920-18924 (1996-08-02)
Polyamine catabolism is rate limited by spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT). Although the amino acid sequence of SSAT is known, the substrate binding and catalytic sites are not. The goal of this study was to define the region responsible for acetyl coenzyme
Biochemistry null
Eileen B Ekstrom et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 69(9), 5414-5422 (2003-09-06)
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in anoxic waters and sediments are the major producers of methylmercury in aquatic systems. Although a considerable amount of work has addressed the environmental factors that control methylmercury formation and the conditions that control bioavailability of inorganic
Short-term variation of nutritive and metabolic parameters in Temora longicornis females (Crustacea, Copepoda) as a response to diet shift and starvation
Tobias Kreibich
Helgoland Marine Research , 62(3), 241-249 (2008)
Agnieszka Jankowska-Kulawy et al.
Neurochemistry international, 57(7), 851-856 (2010-09-21)
Several pathologic conditions are known to cause thiamine deficiency, which induce energy shortages in all tissues, due to impairment of pyruvate decarboxylation. Brain is particularly susceptible to these conditions due to its high rate of glucose to pyruvate-driven energy metabolism.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service