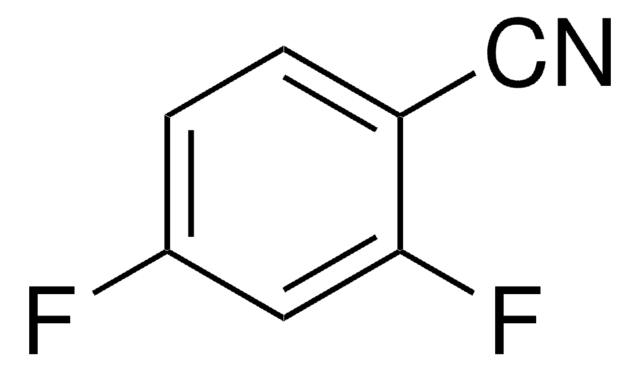
D57558
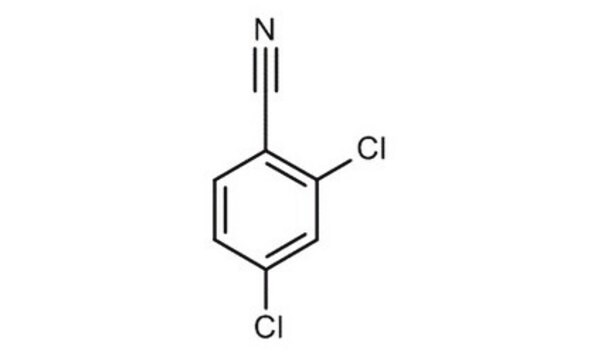
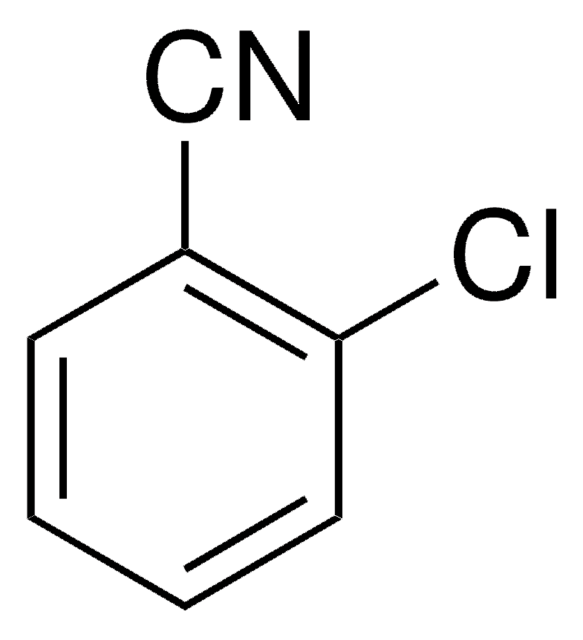
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
97%
Synonym(s):
Dichlobenil
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
Cl2C6H3CN
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
172.01
Beilstein:
1909167
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
powder
mp
143-146 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Clc1cccc(Cl)c1C#N
InChI
1S/C7H3Cl2N/c8-6-2-1-3-7(9)5(6)4-10/h1-3H
InChI key
YOYAIZYFCNQIRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile can be used as a starting material to synthesize:
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzaldehyde using lithium N, N′-dimethylethylenediaminoaluminum hydride as a reducing agent.
- 5-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2H-tetrazole via gold-catalyzed nucleophilic (3 + 2) cycloaddition reaction with sodium azide.
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzamide via hydrolysis using potassium tert-butoxide as a catalyst.
- Chloro-aminoindazole by reacting with hydrazine monohydrate.
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzenecarboselenoamide by treating with Woollins′ reagent.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Aquatic Chronic 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Synthesis of primary arylselenoamides by reaction of aryl nitriles with Woollins' reagent
Hua Guoxiong, et al.
Organic Letters, 8(23), 5251-5254 (2006)
Valeria Franceschini et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 27(4), 825-835 (2009-04-08)
The herbicide dichlobenil selectively causes necrosis of the dorsomedial part of olfactory neuroepithelium (NE) with permanent damage to the underlying mucosa, whereas the lateral part of the olfactory region and the nasal respiratory mucosa remain undamaged. We investigated here whether
L Peng et al.
Plant biology (Stuttgart, Germany), 15(2), 405-414 (2012-07-05)
Cellulose is the major component of plant cell walls and is an important source of industrial raw material. Although cellulose biosynthesis is one of the most important biochemical processes in plant biology, the regulatory mechanisms of cellulose synthesis are still
Fang Xie et al.
Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 272(3), 598-607 (2013-08-08)
We explored the mechanisms underlying the differential effects of two olfactory toxicants, the herbicide 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile (DCBN) and the anti-thyroid drug methimazole (MMZ), on olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) regeneration in mouse olfactory epithelium (OE). DCBN, but not MMZ, induced inflammation-like pathological
Guang-Cai Chen et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 188(1-3), 156-163 (2011-02-18)
The effect of lead on the adsorption of diuron and dichlobenil on multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) was investigated to explore the possible application of MWCNTs for removal of both herbicides from contaminated water. The adsorption of diuron and dichlobenil on
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| D57558-100G | |
| D57558-25G | 4061832108902 |
| D57558-5KG |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service