U6253
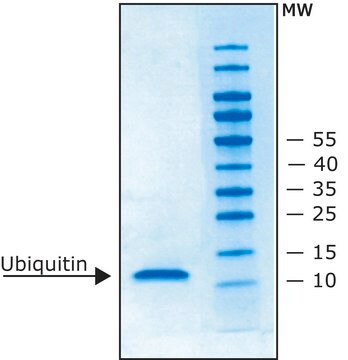
Ubiquitin from bovine erythrocytes
BioUltra, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE), essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
ATP-dependent proteolytic factor, Ub
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine erythrocytes
Quality Level
product line
BioUltra
Assay
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
storage condition
(Tightly closed. Dry)
technique(s)
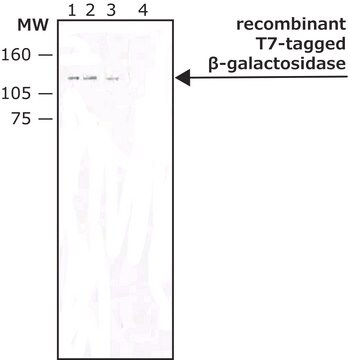
western blot: suitable
impurities
salt, essentially free
solubility
water: 1 mg/mL, clear, colorless
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
bovine ... LOC(101902760)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
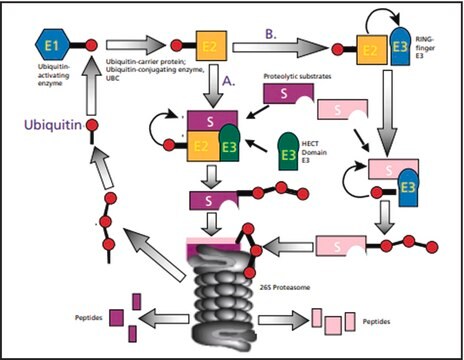
Ubiquitin is a highly conserved regulatory protein. It is found in all eukaryotic cells and is virtually identical across all forms of life including yeast, humans, and plants. ubiquitin structure contains seven Lys residues and an N-terminus, all of which are target sites for ubiquitination.
Application
Ubiquitin from bovine erythrocytes can be used for in vitro ubiquitinylation assay. The product can also be used as a marker in western blotting.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
antibody
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service