N3143
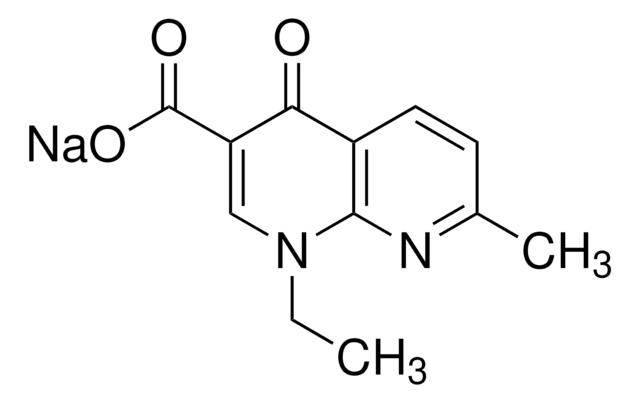
Nalidixic acid sodium salt
powder
Synonym(s):
1-Ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid sodium salt
About This Item
Recommended Products
sterility
γ-irradiated
form
powder
antibiotic activity spectrum
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
Mode of action
DNA synthesis | interferes
enzyme | inhibits
SMILES string
[Na+].CCN1C=C(C([O-])=O)C(=O)c2ccc(C)nc12
InChI
1S/C12H12N2O3.Na/c1-3-14-6-9(12(16)17)10(15)8-5-4-7(2)13-11(8)14;/h4-6H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,16,17);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
ROKRAUFZFDQWLE-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Reconstitution
replaced by
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Repr. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service