M6435
Methionine Aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus
≥93% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
Assay
≥93% (SDS-PAGE)
form
solution
specific activity
0.5 units/mg protein
mol wt
37 kDa by SDS-PAGE
UniProt accession no.
foreign activity
Other proteases, none detected
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 ... PF0541(1468383)
General description
Methionine aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus is a 32 kDa thermostable enzyme. It belongs to type 2a class of methionine aminopeptidase. Methionine aminopeptidase maintains protein homeostasis and coordinates posttranslational modification of proteins in eukaryotes.
X-ray crystallography of the structure of methionine aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus or PfMAP was performed at a resolution of 1.75A and showed that the protein consists of a catalytic domain containing two cobalt ions in the active site and a unique insertion domain which is specific to the prokaryotic form of the protein.
Application
Methionine Aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus has been used in a study to analyze the binding of Co(II)-specific inhibitors to the methionyl aminopeptidases from Escherichia coli and Pyrococcus furiosus. It has also been used in a study to examine the binding of a new class of pseudopeptide analog inhibitors.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Thermostable methionine aminopeptidase, which specifically liberates the N-terminal methioinine from proteins and peptides.
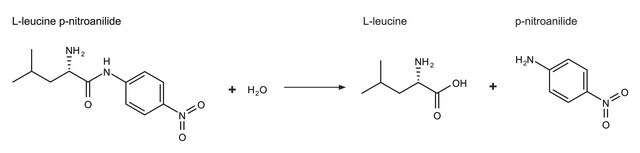
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1 μmol of Met from Met-Pro-Ala-Ala-Gly in 1 minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Solution containing 0.01% Tween® 20, 0.1 mM CoCl2, and 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5.
Legal Information
TWEEN is a registered trademark of Croda International PLC
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Methionine aminopeptidase from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: molecular cloning and overexperssion in Escherichia coli of the gene, and characteristics of the enzyme
Tsunasawa S, et al.
Journal of Biochemistry, 122(4), 843-850 (1997)
Advances in bacterial methionine aminopeptidase inhibition
Helgren TR, et al.
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 16(4), 397-414 (2016)
S Tsunasawa et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 122(4), 843-850 (1997-12-17)
A gene for a methionine aminopeptidase (MAP; EC 3.4.11.18), which catalyzes the removal of amino-terminal methionine from the growing peptide chain on the ribosome, has been cloned from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon, Pyrococcus furiosus, by a novel method effectively using its
T H Tahirov et al.
Journal of molecular biology, 284(1), 101-124 (1998-11-13)
The structure of methionine aminopeptidase from hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMAP) with an optimal growth temperature of 100 degreesC was determined by the multiple isomorphous replacement method and refined in three different crystal forms, one monoclinic and two hexagonal, at resolutions
Sanghamitra Mitra et al.
Journal of biological inorganic chemistry : JBIC : a publication of the Society of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 14(4), 573-585 (2009-02-10)
Methionine aminopeptidases (MetAPs) represent a unique class of protease that is capable of the hydrolytic removal of an N-terminal methionine residue from nascent polypeptide chains. MetAPs are physiologically important enzymes; hence, there is considerable interest in developing inhibitors that can
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service