C2366
Anti-K+/Cl- Cotransporter (KCC2) antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-DEE34, Anti-EIEE34, Anti-EIG14, Anti-KCC2, Anti-hKCC2
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
IgG fraction of antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
species reactivity
canine, rat
technique(s)
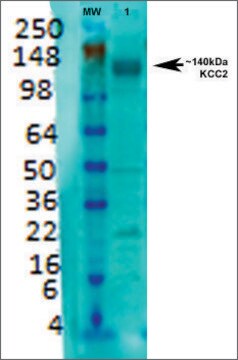
western blot: 0.5-2.0 μg/mL using rat brain membrane preparation
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
rat ... Slc12a5(171373)
General description
Transporters and exchangers play a critical role in the generation and dissipation of action potentials in nerve cells and in the maintenance of normal cell volume. They are also involved in a variety of mechanisms pertaining to the control of neuronal growth, maturation, synaptic plasticity and neuroendocrine functions
The cation-chloride cotransporters (CCCs) are glycoproteins involved in transport of ions, including chloride, across the cell membrane without an accompanying net charge movement; thus this type of transport is driven without the direct hydrolysis of ATP. The energy for the transport is derived from the cation gradient generated by the Na+/K+/ATPase. The CCCs also play a critical role in influencing GABA- and glycine-mediated signaling. Other transporters that participate in chloride homeostasis include Na+-dependent and Na+-independent anion exchangers, which exchange chloride for HCO3- ions
Three cotransporters belonging to this family include sodiumchloride( Na+/Cl-/ ) cotransporters (NCCs), sodiumpotassium-chloride (Na+/K+/2Cl-) cotransporters (NKCCs) and potassium-chloride (K+/Cl-) cotransporters (KCCs). K+/Cl- cotransporter (KCC2) is the major neuronal chloride transporter. It has been proposed to play a role in the modulation of neuronal responses to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA-mediated fasthyperpolarizing inhibition depends on extrusion of chloride by KCC2 In conditions of neuronal damage, where neuronal excitability is increased, and in spinal cord in models of neuropathic pain, the expression of the KCC2 transporter is decreased
The cation-chloride cotransporters (CCCs) are glycoproteins involved in transport of ions, including chloride, across the cell membrane without an accompanying net charge movement; thus this type of transport is driven without the direct hydrolysis of ATP. The energy for the transport is derived from the cation gradient generated by the Na+/K+/ATPase. The CCCs also play a critical role in influencing GABA- and glycine-mediated signaling. Other transporters that participate in chloride homeostasis include Na+-dependent and Na+-independent anion exchangers, which exchange chloride for HCO3- ions
Three cotransporters belonging to this family include sodiumchloride( Na+/Cl-/ ) cotransporters (NCCs), sodiumpotassium-chloride (Na+/K+/2Cl-) cotransporters (NKCCs) and potassium-chloride (K+/Cl-) cotransporters (KCCs). K+/Cl- cotransporter (KCC2) is the major neuronal chloride transporter. It has been proposed to play a role in the modulation of neuronal responses to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA-mediated fasthyperpolarizing inhibition depends on extrusion of chloride by KCC2 In conditions of neuronal damage, where neuronal excitability is increased, and in spinal cord in models of neuropathic pain, the expression of the KCC2 transporter is decreased
Specificity
Anti-K+/Cl- Cotransporter (KCC2) specifically recognizes K+/Cl- cotransporter. Wide range of species cross-reactivity expected due to sequence homology.
Wide range of species cross-reactivity expected due to sequence homology.
Immunogen
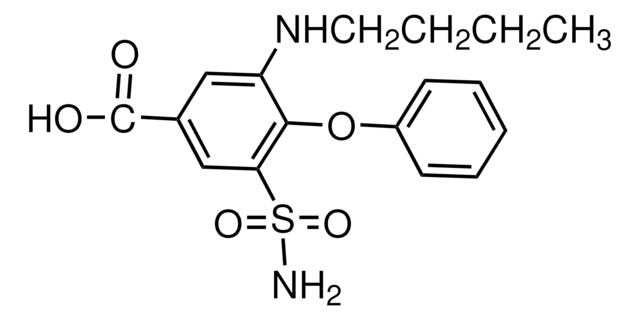
N-terminal His-tag fusion protein corresponding to residues 932-1043 of rat K+/Cl- Cotransporter (KCC2).
Application
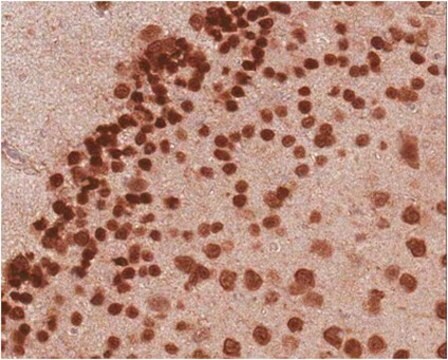
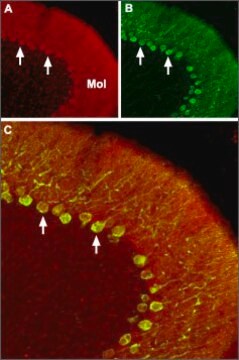
Anti-K+/Cl- Cotransporter (KCC2) specifically recognizes K+/Cl- cotransporter in rat brain membrane preparations by immunoblotting and Madin Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells by immunocytochemistry.
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Immunocytochemistry (1 paper)
Immunocytochemistry (1 paper)
Target description
Anti-K+/Cl- Cotransporter (KCC2) specifically recognizes K+/Cl- cotransporter (KCC2). The cation-chloride cotransporters (CCCs) are glycoproteins involved in transport of ions, includingchloride, across the ce
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Ehud Chorin et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 31(36), 12916-12926 (2011-09-09)
Vesicular Zn(2+) regulates postsynaptic neuronal excitability upon its corelease with glutamate. We previously demonstrated that synaptic Zn(2+) acts via a distinct metabotropic zinc-sensing receptor (mZnR) in neurons to trigger Ca(2+) responses in the hippocampus. Here, we show that physiological activation
John A Payne et al.
Trends in neurosciences, 26(4), 199-206 (2003-04-12)
Electrical signaling in neurons is based on the operation of plasmalemmal ion pumps and carriers that establish transmembrane ion gradients, and on the operation of ion channels that generate current and voltage responses by dissipating these gradients. Although both voltage-
Begonia M Morales-Aza et al.
Neurobiology of disease, 17(1), 62-69 (2004-09-08)
Cation chloride cotransporters have been proposed to play a role in the modulation of neuronal responses to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In conditions of neuronal damage, where neuronal excitability is increased, the expression of the KCC2 transporter is decreased. This is
Claudio Rivera et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 24(19), 4683-4691 (2004-05-14)
GABA-mediated fast-hyperpolarizing inhibition depends on extrusion of chloride by the neuron-specific K-Cl cotransporter, KCC2. Here we show that sustained interictal-like activity in hippocampal slices downregulates KCC2 mRNA and protein expression in CA1 pyramidal neurons, which leads to a reduced capacity
The membrane trafficking and functionality of the K+-Cl- co-transporter KCC2 is regulated by TGF-β2.
Eleni Roussa et al.
Journal of cell science, 129(18), 3485-3498 (2016-08-10)
Functional activation of the neuronal K(+)-Cl(-) co-transporter KCC2 (also known as SLC12A5) is a prerequisite for shifting GABAA responses from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing during development. Here, we introduce transforming growth factor β2 (TGF-β2) as a new regulator of KCC2 membrane
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service