A8679
Anti-Aflatoxin B1 antibody produced in rabbit
fractionated antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-Aflatoxin B1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.46
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
fractionated antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
capture ELISA: 1:4,000 using aflatoxin B1-BSA
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Aflatoxin B1 is the most abundant and significant member of the group, which includes B2, B2a, G1, G2a, M1, M2, P1, Q1, aflatoxicol I (natural isomer), aflatoxicol II (unnatural isomer), tetrahydrodeoxy aflatoxin B1, and the unstable reactive B1 (8,9)-epoxide.
Aflatoxins are highly carcinogenic.
Aflatoxins are highly toxic mycotoxins produced by the fungus Aspergillus. Aflatoxins are commonly found in various grains and peanut butter.
Mycotoxins, a group of chemically diverse secondary fungal metabolites, induce a variety of toxic responses in humans and animals when food and feed containing these compounds are ingested. Rapidly quantitating levels of mycotoxin contamination can help reduce exposure to these toxins.
The antibody reacts with the B1 aflatoxin and also recognizes aflatoxins G1, B2, and the KLH protein. No cross-reaction is observed with aflatoxins and B2a, G2, G2a, M1.
Specificity
Sensitivity range for this product is 0.005-20 ng/ml of aflatoxin B1.
Immunogen
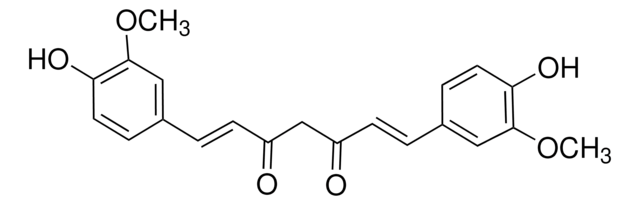
aflatoxin B1-KLH.
Application
Rabbit Anti-Aflatoxin B1 antibody has been used for the development of electrochemical immunosensors. The antibody has also been used in designing novel sandwich immunoassays. The product can also be used for capture ELISA at a dilution of 1:1,000.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aflatoxin B1 and its metabolites act as potent carcinogens, mutagens and teratogens. Aflatoxins have been implicated in human hepatocellular carcinoma, outbreaks of aflatoxicosis, Rey′s syndrome, chronic hepatitis and increased mortality from infection in animal husbandry.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Joseph H O Owino et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 388(5-6), 1069-1074 (2007-06-15)
Aflatoxins are a group of mycotoxins that have deleterious effects on humans and are produced during fungal infection of plants or plant products. An electrochemical immunosensor for the determination of aflatoxin B(1) (AFB(1)) was developed with AFB(1)antibody (AFB(1)-Ab) immobilized on
C G Caratsch et al.
Neuroscience letters, 111(3), 344-350 (1990-04-06)
The effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on synaptic mechanisms were studied at the frog neuromuscular junction by using classical electrophysiological techniques. CGRP reduced the quantal content of evoked neurotransmitter release, as well as the sensitivity of postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine
An over review on effect of aflatoxin in animal husbandry
Talebi E, et al.
Asian journal of experimental biological sciences, 2(3), 754-757 (2011)
Jeong Moon et al.
Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 18(2) (2018-02-22)
Aflatoxins (AFs) are highly toxic compounds that can cause both acute and chronic toxicity in humans. Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is considered the most toxic of AFs. Therefore, the rapid and on-site detection of AFB1 is critical for food safety management.
J F Alberts et al.
International journal of food microbiology, 135(1), 47-52 (2009-08-18)
The enzymatic degradation of aflatoxin B(1) (AFB(1)) by white rot fungi through laccase production was investigated in different liquid media. A significant (P<0.0001) correlation was observed between laccase activity and AFB(1) degradation exhibited by representatives of Peniophora and Pleurotus ostreatus
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service