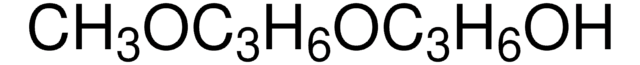538221
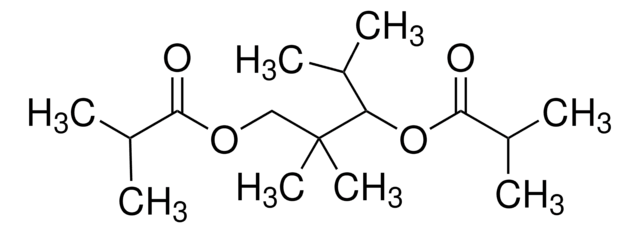
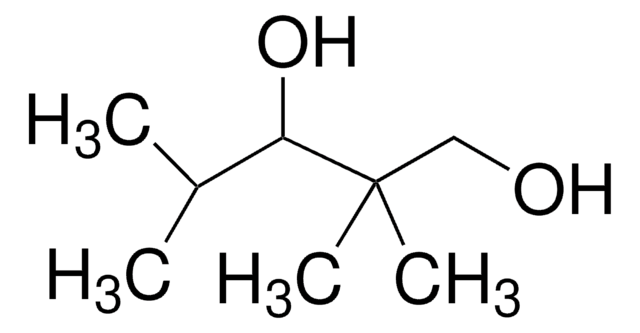
2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate
mixture of isomers, 99%
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
(CH3)2CHCH[O(R)]C(CH3)2CH2O(R), R=-COCH(CH3)2 or H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
216.32
EC Number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352001
NACRES:
NA.21
Assay:
99%
technique(s):
GC/MS: suitable
bp:
255 °C (lit.)
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
liquid
technique(s)
GC/MS: suitable
impurities
≤0.10% (water)
refractive index
n20/D 1.441 (lit.)
bp
255 °C (lit.)
mp
−50 °C (lit.)
density
0.95 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
InChI
1S/C12H24O3/c1-8(2)10(13)12(5,6)7-15-11(14)9(3)4/h8-10,13H,7H2,1-6H3
InChI key
DAFHKNAQFPVRKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate (TMPD-MIB, texanol), a volatile organic compound (VOC), is an important component found in paints and printing inks. It is utilized as a coalescing agent to reduce the minimal film forming temperature (MFFT) during latex film preparation. Its detection in polypropylene packed food samples has been reported by coupled capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HRGC-MS). The performance of various dispersant affecting the dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) in texanol has been studied.
Application
2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate (texanol) may be used in the prepare carbon nanotube (CNT) paste employed in field emission displays (FED).
Legal Information
Manufactured by Eastman Chemical Company. Distributed by Aldrich Chemical Company.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
251.6 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
122 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Milling and dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in texanol.
Darsono N, et al.
Applied Surface Science, 254(11), 3412-3419 (2008)
Occurrence of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate (Texanol?) in foods packed in polystyrene and polypropylene cups.
Kempf M, et al.
Food Additives and Contaminants, 26(4), 563-567 (2009)
Asthma and the indoor environment: the significance of emission of formaldehyde and volatile organic compounds from newly painted indoor surfaces.
Wieslander, G, et al.
International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 69(2), 115-124 (1996)
Film formation from monodisperse acrylic latices: 5. Drying and ageing in coalescing agent containing latex films.
Zohrehvand S and te Nijenhuis T.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 288(1), 75-82 (2005)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service