C24604
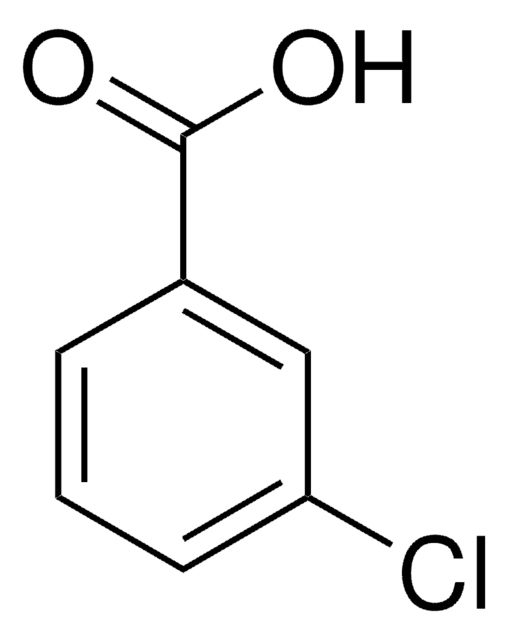
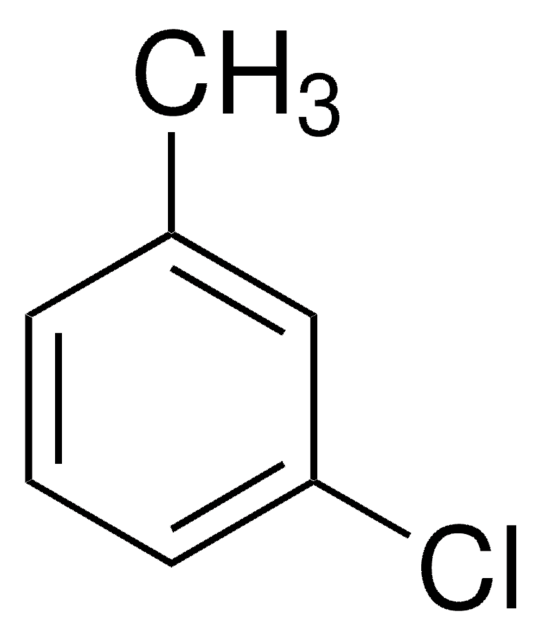
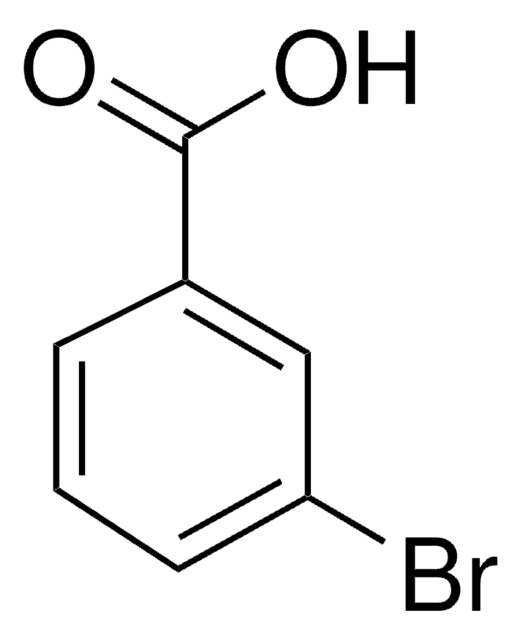
3-Chlorobenzoic acid
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Synonym(s):
m-Chlorobenzoic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
ClC6H4CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
156.57
Beilstein:
907218
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
product line
ReagentPlus®
Assay
≥99%
form
powder
mp
153-157 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
OC(=O)c1cccc(Cl)c1
InChI
1S/C7H5ClO2/c8-6-3-1-2-5(4-6)7(9)10/h1-4H,(H,9,10)
InChI key
LULAYUGMBFYYEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Legal Information
ReagentPlus is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
V P Jayachandran et al.
Journal of industrial microbiology & biotechnology, 36(2), 219-227 (2008-10-23)
The compatibility and efficiency of two ortho-cleavage pathway-following pseudomonads viz. the 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CBA)-degrader, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3mT (3mT) and the phenol-degrader, P. stutzeri SPC-2 (SPC-2) in a mixed culture for the degradation of these substrates singly and simultaneously in mixtures was
Caroline Laemmli et al.
Archives of microbiology, 181(2), 112-121 (2003-12-17)
Ralstonia eutropha JMP134 possesses two sets of similar genes for degradation of chloroaromatic compounds, tfdCDEFB (in short: tfdI cluster) and tfdDII CII EII FII BII (tfdII cluster). The significance of two sets of tfd genes for the organism has long
Hee-Sung Bae et al.
Chemosphere, 55(1), 93-100 (2004-01-15)
An anaerobic continuous-flow fixed-bed column reactor capable of degrading 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CBA) under denitrifying conditions was established, and its rate reached 2.26 mM d(-1). The denitrifying population completely degraded 3-CBA when supplied at 0.1-0.54 mM, but its activity was partly suppressed
Nicole Trefault et al.
International microbiology : the official journal of the Spanish Society for Microbiology, 12(2), 97-106 (2009-09-29)
Cupriavidus necator JMP134 has been extensively studied because of its ability to degrade chloroaromatic compounds, including the herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 3-chlorobenzoic acid (3-CB), which is achieved through the pJP4-encoded chlorocatechol degradation gene clusters: tfdCIDIEIFI and tfdDIICIIEIIFII. The present
Alfredo Gallego et al.
World journal of microbiology & biotechnology, 28(3), 1245-1252 (2012-07-19)
An indigenous strain of Pseudomonas putida capable of degrading 3-chlorobenzoic acid as the sole carbon source was isolated from the Riachuelo, a polluted river in Buenos Aires. Aerobic biodegradation assays were performed using a 2-l microfermentor. Biodegradation was evaluated by
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service