490644
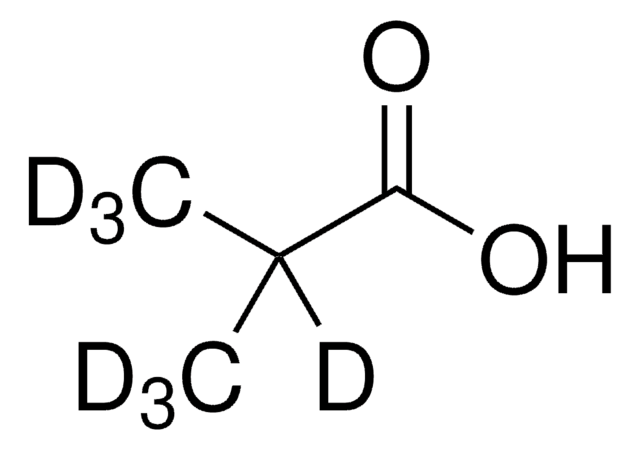
Propionic acid-d6
98 atom % D
Synonym(s):
Propanoic acid-d6
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
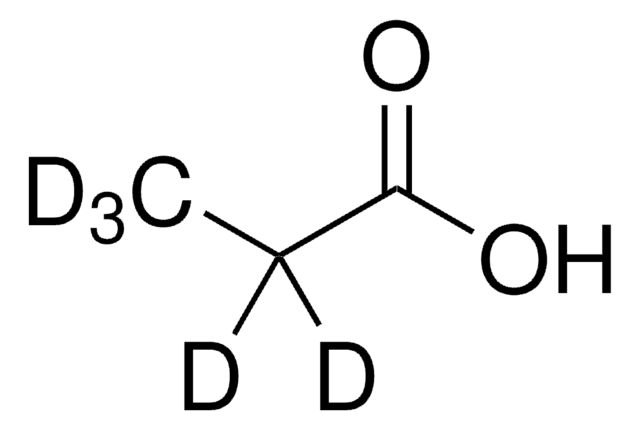
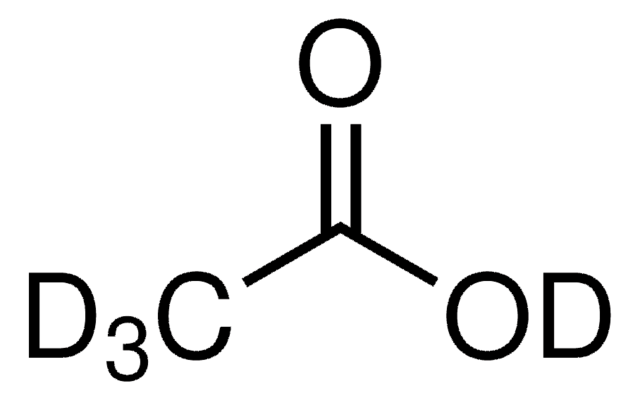
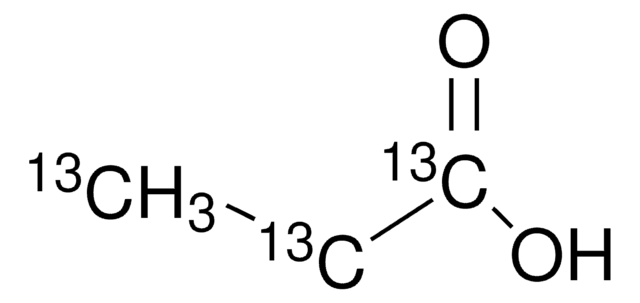
CD3CD2CO2D
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
80.12
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352106
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.12
Recommended Products
isotopic purity
98 atom % D
Quality Level
Assay
99% (CP)
refractive index
n20/D 1.386 (lit.)
bp
141 °C (lit.)
mp
−24-−23 °C (lit.)
density
1.072 g/mL at 25 °C
mass shift
M+6
SMILES string
[2H]OC(=O)C([2H])([2H])C([2H])([2H])[2H]
InChI
1S/C3H6O2/c1-2-3(4)5/h2H2,1H3,(H,4,5)/i1D3,2D2/hD
InChI key
XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-WYMDYBCKSA-N
Related Categories
Packaging
This product may be available from bulk stock and can be packaged on demand. For information on pricing, availability and packaging, please contact Stable Isotopes Customer Service.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1B - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
129.2 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
54 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Bjoern O Schroeder et al.
Cell host & microbe, 23(1), 27-40 (2017-12-26)
Diet strongly affects gut microbiota composition, and gut bacteria can influence the colonic mucus layer, a physical barrier that separates trillions of gut bacteria from the host. However, the interplay between a Western style diet (WSD), gut microbiota composition, and
Petia Kovatcheva-Datchary et al.
Cell reports, 26(13), 3772-3783 (2019-03-28)
The gut microbiota can modulate human metabolism through interactions with macronutrients. However, microbiota-diet-host interactions are difficult to study because bacteria interact in complex food webs in concert with the host, and many of the bacteria are not yet characterized. To
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service