SML1740
FIN56
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
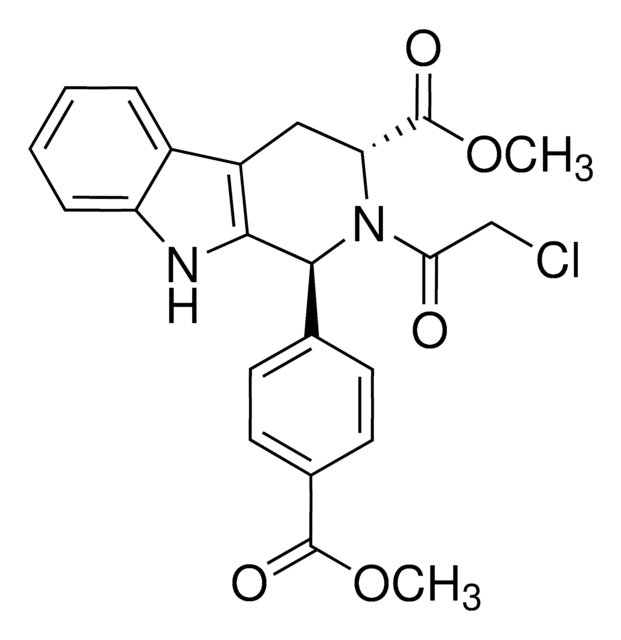
N2,N7-Dicyclohexyl-9-(hydroxyimino)-9H-fluorene-2,7-disulfonamide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C25H31N3O5S2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
517.66
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white to beige
solubility
DMSO: 20 mg/mL, clear
storage temp.
room temp
Biochem/physiol Actions
FIN56 is a specific inducer of ferroptosis, a non-apoptotic form of cell death characterized by iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxidation products and lethal reactive oxygen species (ROS). FIN56 has an EC50 value of 240 nM, and is believed to act though two separate pathways. The first requires the enzymatic activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC),and results in degradation of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which acts as a negative regulator of ferroptosis by reducing lipid hydroperoxides. The second pathway involves FIN56 binding to and activing squalene synthase, which leads to coenzyme Q10 depletion.
Ferroptosis inducer 56 (FIN56) is a member of the class 3 ferroptosis inducers.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Unsolved mysteries: How does lipid peroxidation cause ferroptosis?.
Feng H and Stockwell BR
PLoS Biology, 16(5), e2006203-e2006203 (2018)
Po-Han Chen et al.
Cell death and differentiation, 27(3), 1008-1022 (2019-07-20)
Ferroptosis is a specialized iron-dependent cell death that is associated with lethal lipid peroxidation. Modulation of ferroptosis may have therapeutic potential since it has been implicated in various human diseases as well as potential antitumor activities. However, much remains unknown
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service