MAK107
LCAT Activity Assay Kit
Supplied by Roar Biomedical, Inc.
Synonym(s):
Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity assay kit
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 100 fluorometric tests
application(s)
pharmaceutical
detection method
fluorometric
relevant disease(s)
cardiovascular diseases
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... LCAT(3931)
General description
The plasma protein lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) catalyzes the transfer of an acyl group from the sn2 position of phosphatidylcholine to the 3-hydroxyl group of cholesterol resulting in the formation cholesteryl ester. This enzymatic activity occurs on the surface of high density lipoprotein (HDL). The cholesteryl esters formed by LCAT may be packed into the core of HDL.
Application
Applications for this method include high-throughput screening, mechanism of action studies and structure-activity relationship (SAR) work.
LCAT Activity Assay Kit has been used for measuring lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase activity in plasma samples.
Features and Benefits
Compatible with high-throughput handling systems.
Suitability
Suitable for measuring phospholipase activity of LCAT in plasma or serum.
Principle
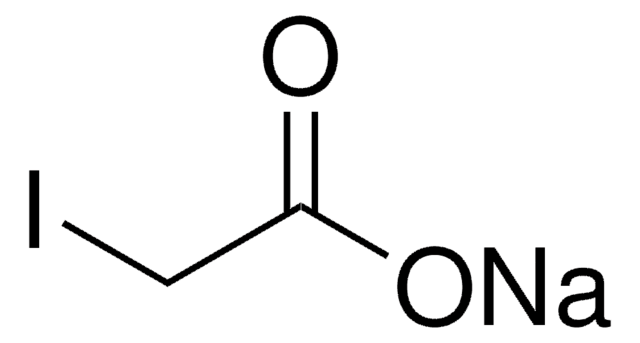
The LCAT Activity Assay Kit is a fluorometric assay useful for measuring phospholipase activity of (λEx=390 nm/λEm=470 nm) LCAT. The assay may be validated by inhibition of LCAT with iodoacetate or another spectrally benign (not Ellman′s reagent) LCAT inhibitor.
Kit Components Only
Product No.
Description
- Substrate Reagent .1 mL
- READ Reagent 30 mL
- LCAT Assay Buffer 20 mL
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Flam. Liq. 2 - STOT SE 1
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
Flash Point(F)
49.5 °F
Flash Point(C)
9.7 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Reversal of high fat diet-induced obesity through modulating lipid metabolic enzymes and inflammatory markers expressions in rats.
Uddandrao V V S, et al.
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry, 1-7 (2018)
Anatol Kontush et al.
Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 27(8), 1843-1849 (2007-06-16)
The purpose of this study was to define heterogeneity in the molecular profile of lipids, including sphingomyelin and sphingosine-1-phosphate, among physicochemically-defined HDL subpopulations and potential relevance to antiatherogenic biological activities of dense HDL3. The molecular profile of lipids (cholesteryl esters
Yan Ru Su et al.
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 8(4), 576-583 (2003-10-08)
The antiatherogenic effect of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and its major protein component apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) has been largely attributed to their key roles in reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) and cellular cholesterol efflux. Substantial evidence shows that overexpression of human apoA-I
E Nobécourt et al.
Diabetologia, 48(3), 529-538 (2005-02-25)
Elevated oxidative stress, hyperglycaemia, and dyslipidaemia involving low levels of HDL particles are key proatherogenic factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus. We examined the relationship of oxidative stress, and the degree of glycaemia and triglyceridaemia, to antioxidative function of HDL
Ameliorative potential of gingerol: Promising modulation of inflammatory factors and lipid marker enzymes expressions in HFD induced obesity in rats.
Naidu P B, et al.
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 419, 139-147 (2016)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service