C2624
Carbonic Anhydrase from bovine erythrocytes
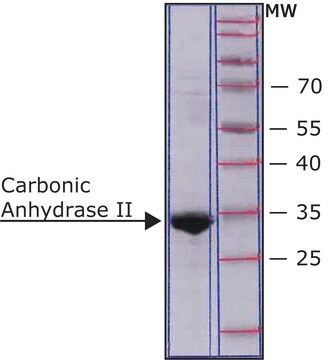
≥95% (SDS-PAGE), specific activity ≥3,500 W-A units/mg protein, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Carbonic Anhydrase from bovine erythrocytes, Carbonate Dehydratase, Carbonate Hydrolyase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine erythrocytes
Assay
≥75% protein basis (biuret)
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥3,500 W-A units/mg protein
solubility
deionized water: >10 mg/mL
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Carbonic anhydrase, from bovine erythrocytes, is used to create carbon dioxide capture systems and to research various purification techniques . Carbonic anhydrase is also used to study acid-base regulation in fish and carbonic anhydrase type II deficiency syndrome .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Carbonic Anhydrase is a zinc-containing enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate. One of its main physiological roles is to maintain the acid-base balance in blood and other tissues. Lack of carbonic anhydrase results in carbonic anhydrase type II deficiency syndrome, which is an autosomal recessive disease that causes osteopetrosis, renal tubular acidosis and brain calcifications .
Unit Definition
One Wilbur-Anderson (W-A) unit will cause the pH of a 0.02 M Trizma buffer to drop from 8.3 to 6.3 per min at 0°C. (One W-A unit is essentially equivalent to one Roughton-Booth unit.)
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Nicolas Ghéczy et al.
RSC advances, 10(32), 18655-18676 (2020-05-18)
Enzyme-catalysed cascade reactions in flow-through systems with immobilised enzymes currently are of great interest for exploring their potential for biosynthetic and bioanalytical applications. Basic studies in this field often aim at understanding the stability of the immobilised enzymes and their
Joana da Costa Ores et al.
Chemosphere, 88(2), 255-259 (2012-04-20)
This work presents a study of industrially applicable techniques to obtain a biologically supported carbon dioxide capture system, based on the extraction of carbonic anhydrase from bovine blood. Carbonic anhydrase is a metalloenzyme which catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon
K M Gilmour et al.
The Journal of experimental biology, 212(Pt 11), 1647-1661 (2009-05-19)
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) is the zinc metalloenzyme that catalyses the reversible reactions of CO(2) with water. CA plays a crucial role in systemic acid-base regulation in fish by providing acid-base equivalents for exchange with the environment. Unlike air-breathing vertebrates, which
Thomas M Bosley et al.
Brain : a journal of neurology, 134(Pt 12), 3502-3515 (2011-11-29)
Carbonic anhydrase type II deficiency syndrome is an uncommon autosomal recessive disease with cardinal features including osteopetrosis, renal tubular acidosis and brain calcifications. We describe the neurological, neuro-ophthalmological and neuroradiological features of 23 individuals (10 males, 13 females; ages at
Marco Catalano et al.
Analytical chemistry, 92(15), 10822-10829 (2020-07-04)
The availability of reliable methods for the characterization of the binding of small molecule ligands to protein targets is crucially important for drug discovery. We have adapted a method, routinely used for the characterization of monoclonal antibodies (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service