A8960
L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate sesquimagnesium salt hydrate
≥95%
Synonym(s):
MAP, Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
form
powder
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
color
white to off-white
solubility
water: 50 mg/mL
storage temp.
room temp
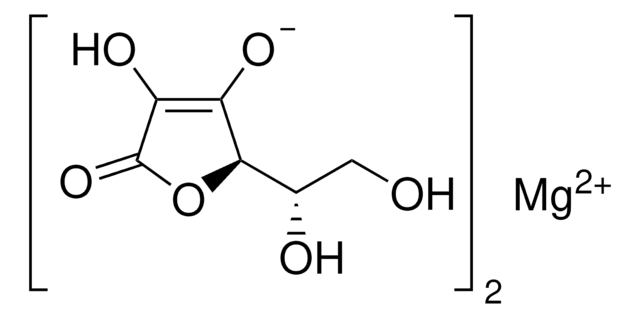
SMILES string
O=C1O[C@@]([C@@H](O)CO)([H])C([O-])=C1OP([O-])([O-])=O.O=C2O[C@@]([C@@H](O)CO)([H])C([O-])=C2OP([O-])([O-])=O.O.[Mg+2].[Mg+2].[Mg+2]
InChI
1S/2C6H9O9P.3Mg.H2O/c2*7-1-2(8)4-3(9)5(6(10)14-4)15-16(11,12)13;;;;/h2*2,4,7-9H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13);;;;1H2/q;;3*+2;/p-6/t2*2-,4+;;;;/m00..../s1
InChI key
HKRNHMZODRSAPN-IXNKEUJHSA-H
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Moreover, MAP plays a pivotal role in metabolomics and biochemical research. Acting as an antioxidant, it effectively scavenges free radicals, offering protection against oxidative damage. Its anti-inflammatory properties contribute to the reduction of inflammation, and studies have indicated its ability to stimulate collagen production. Additionally, MAP serves as a chelating agent, further expanding its applications in various research studies. The multifaceted nature of MAP makes it a valuable tool in scientific investigations, contributing to advancements in cell biology, metabolomics, and biochemical research.
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
- Can be used in Cell Biology, Metabolomics and Biochemical research
- High-quality compound suitable for multiple research applications
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service